IV.
Effectiveness of Fiscal Policy
A. Timing
1.
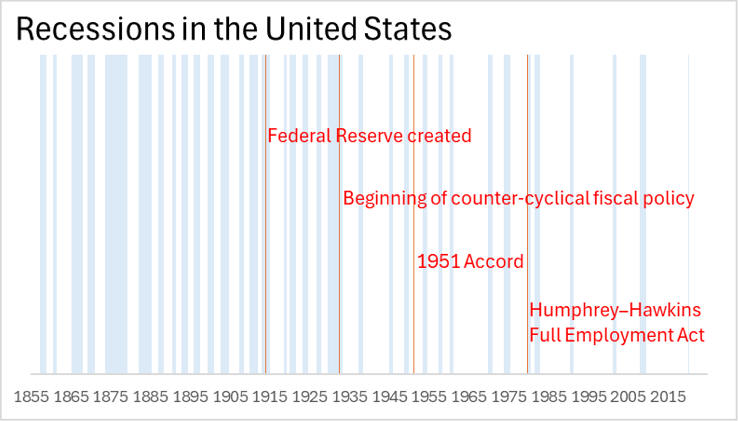
Determining when recessions begin is difficult.
a. Disagreement over
whether the U.S. was in
a recession from 1989-1991 resulted
in little
fiscal action
being taken.
b. The 2001 slowdown happened so fast there
was not time for preemptive action.
2.
Fiscal policy takes time to implement
3. There will be a
delay because it takes business
time to expand capital investment.
B. Political
considerations
1.
Some spending programs are difficult to cut
(social security,
military, education).
2.
Expansionary bias: people vote to spend but
not to tax.
3.
Political business cycle: it is difficult
to accomplish anything
economically
constructive during
an election year
C. Recently, many
felt the federal
debt is too big
and has rendered fiscal policy ineffective.
Its success in
ending the 2001
recession has
yet to be determined although the Federal
budget surplus certainly makes it easier to
increase federal
spending and decrease
taxes although the expense of fighting three
wars has
again increased the deficit.
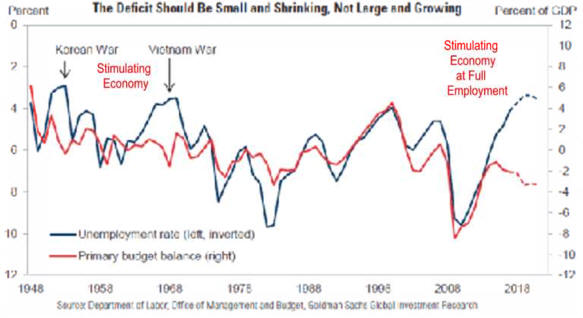
D. In 2012 People Fear the
Drag of Taking Away
the
Stimulus of 2009- 2011.
E.
Kansas Fiscal Policy
Tax Cut Failed
10//17
B Ritholtz
F.
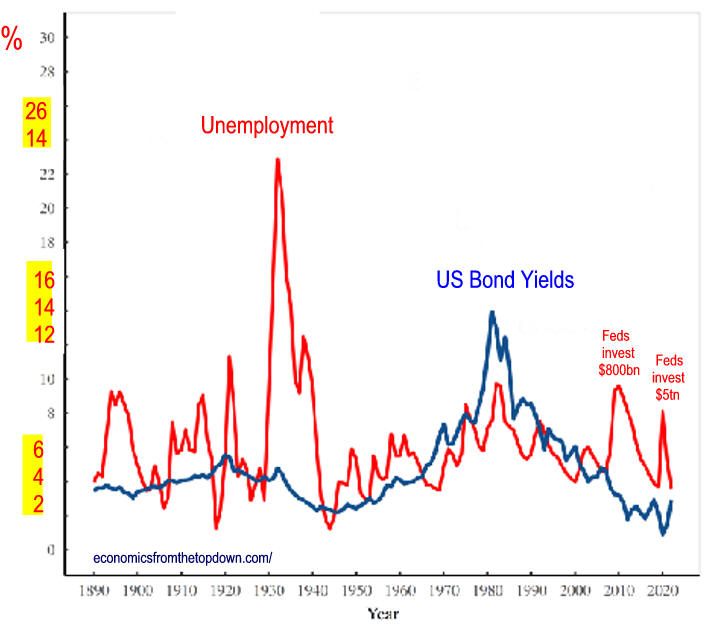
Fed Uncertainty of Economic Effects Of Tax Cuts.
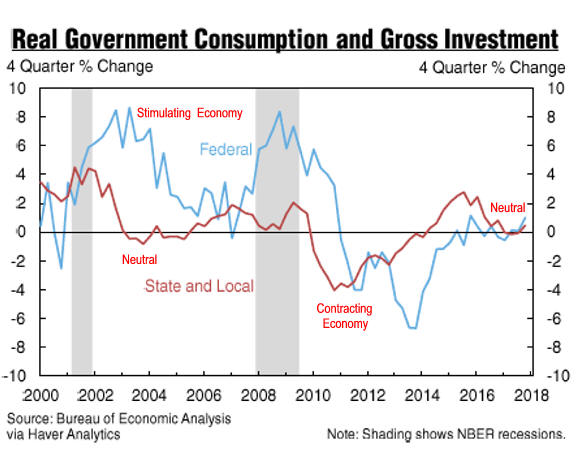
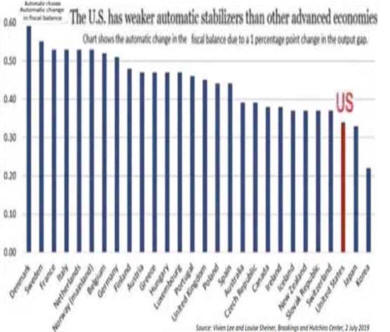
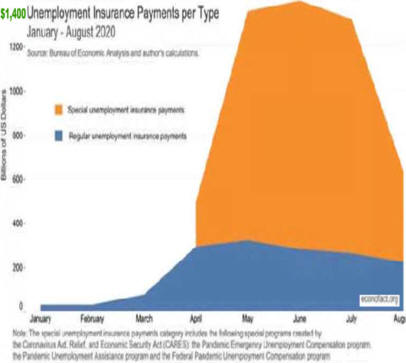
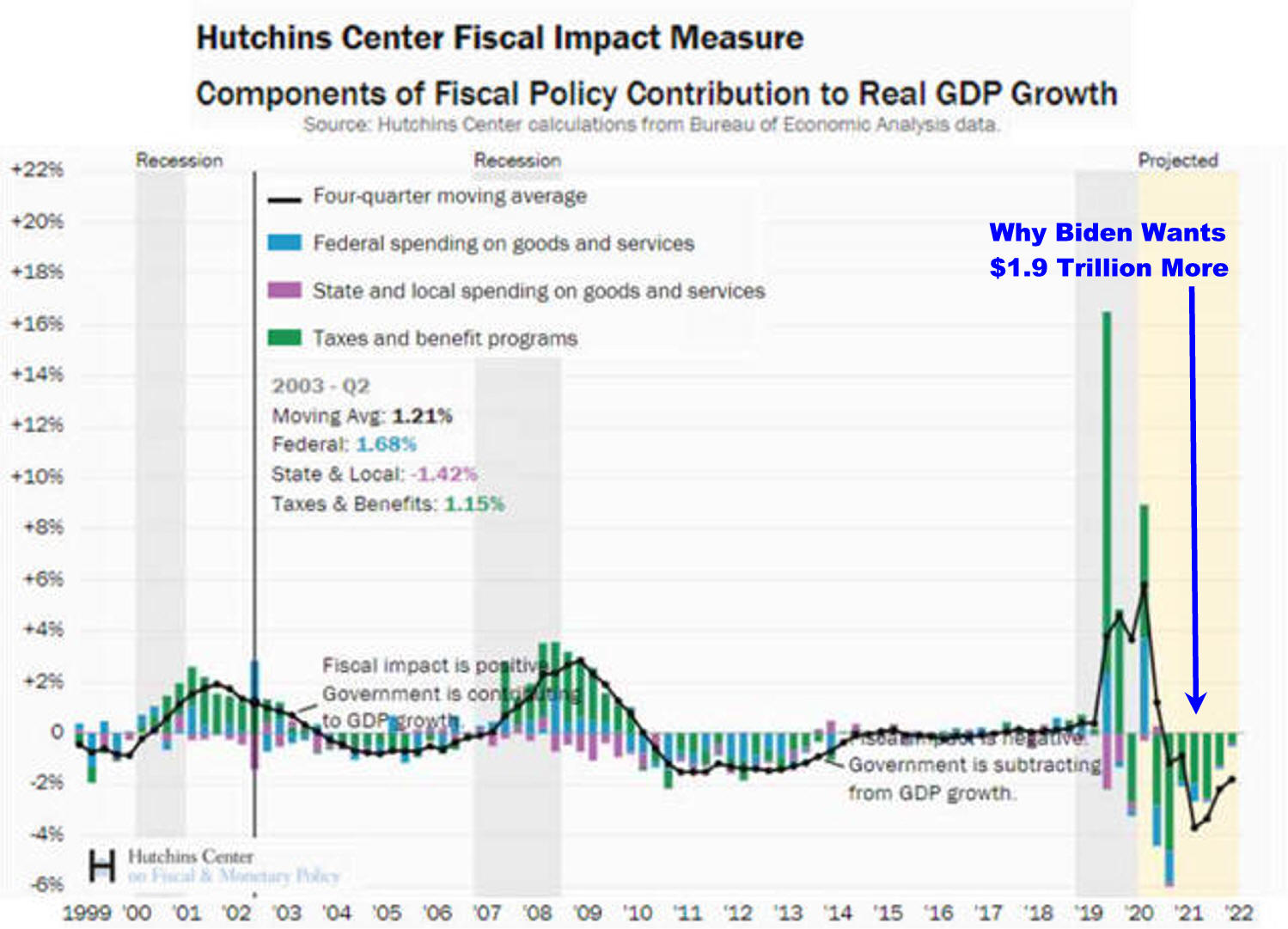
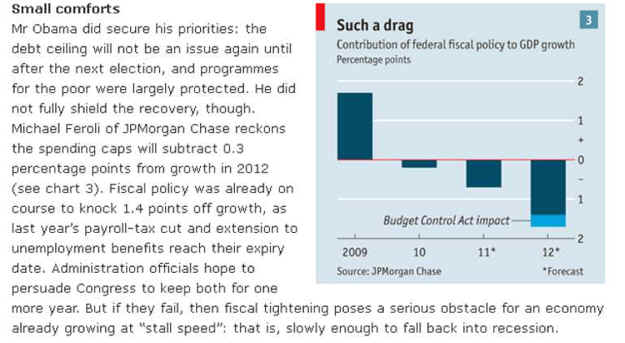
See Chart State and local cuts have very nearly run their course at this
point, but the economy now faces the run-off of stimulus programmers, as well as
the expiration of emergency unemployment benefits and, potentially, the
expiration of lots of other tax proposals. The President's latest plan aims to
move the total government impact on growth from a drag of about 1.5 percentage
points of GDP to approximately even. When the economy is growing at between 1%
and 2% per year, a 1.5 percentage point drag on output is a very big deal
indeed.
See
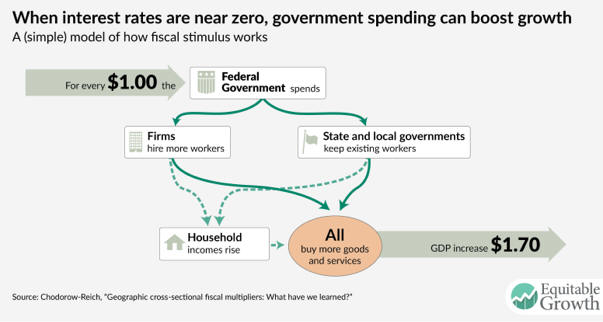
Government Spending Might Not Create Jobs Even During Recessions
V.
Fiscal Policy Affects the Private Economy
A. Until recently,
government borrowing increased the
demand for loanable funds causing higher long-term
interest rates.
1. Crowding out is
the term used to describe how
high rates due to government
borrowing lower
private investment.
2. Many feel
high economic growth of the late
1990's resulted because of low interest rates
caused by federal fiscal responsibility.
B. In the early 1990 people were people are concerned
about the fiscal
drag caused by a federal surplus.
C.
Can
Fiscal Policy Stabilize Output
D.
Trump Tax Act Still and Trickle Down Economics

Source: Seven Deadly Innocent Frauds of Economic Policy - Warren Mosler pdf
Lecture
from W. Moster 62 min video
Video Interview
VI. Deadly Innocent Sins Frauds of
Economic Policy

|
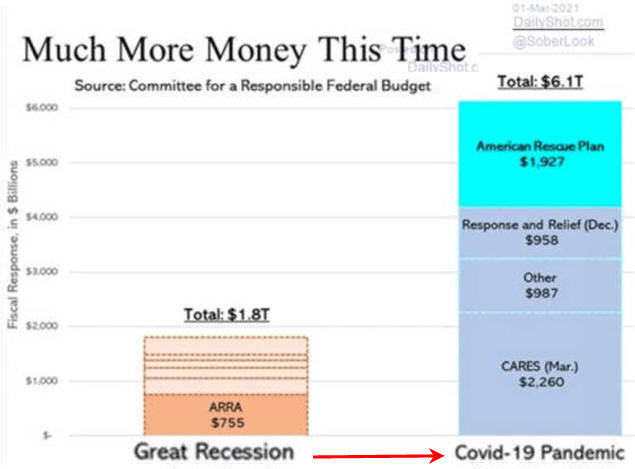
Biden Wants More
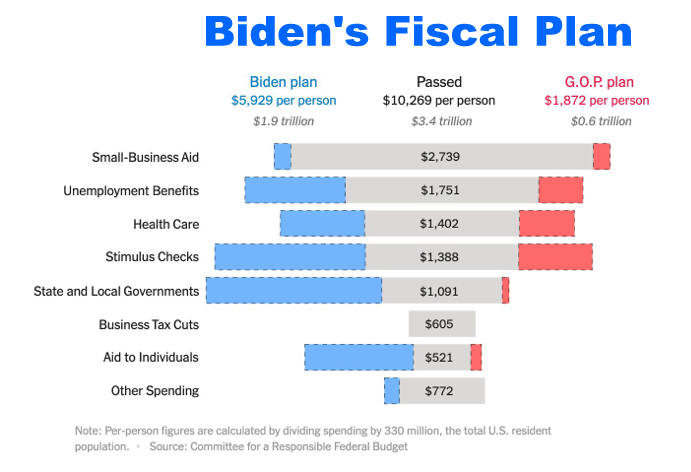
Here is Why
Hutchins Center Fiscal Impact Measure
Modern Money & Public Purpose
1: The Historical Evolution of Money and Debt
2: Governments Are Not Households
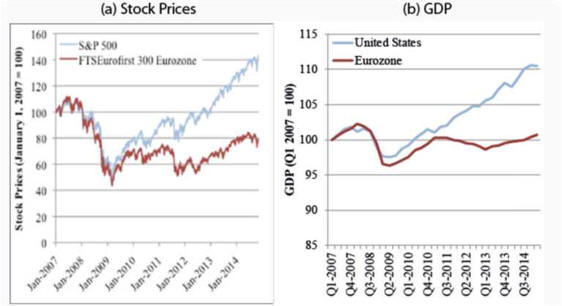
3: The Eurozone
4. Real vs. Nominal Economy
The Other Side of the Story
MMT vs. Austrian School Debate
Minsky, Inequality, and the Monetary:Fiscal Policy Outlook
Modern Monetary Theory Videos
Demystifying Modern Monetary
What Modern Monetary Theory Tells Us About Econ Policy
Why the Elite are Living In an Economic Fantasy
|