|
Lecture Notes
I. Functions of Money
Review Functions of Monet are a Medium of Exchange, Standard of Value, Store of Value
II. Supply and Demand for Money A. Three categories of the supply of money 1. M1 = Currency, coins, and demand deposits. 2. M2 = M1 plus near monies such as small time deposits (savings accounts) and short-term government securities 3. M3 = M2 plus large time deposits (over $100,000) B. What backs the dollar? 1. In 1971 President Nixon took the U.S. off a partial gold standard. See The Gold Reserve Act 2. It is a debt of the federal government. 3. Faith in the government's ability to maintain value. 4. Value is determined by acceptability -it's legal tender). 5. Commodity money, such as tobacco used as money in the Virginia colony, has intrinsic value of its own. 6. It's fiat (by decree of the government) money. C. Fiat money's first appearance in the U.S. when Congress issued Continental currency with no gold backing 1. Gresham's Law (bad money chases good) caused it to disappear during periods of high inflation. 2. Problem when war is financed by printing 3. Latest US example was Vietnam War 4. State issued their own money. 5. Ben Franklin on Paper Money Economy 6. Greenbacks (green Treasury demand notes) were issued as legal tender during the Civil War. a. An return to Gold Standard requiring the government owns enough gold to back U.S. currency. b. Printing money was used to finance much of the War c. Returning to gold slowed government spending financed by debt. d. In 1971 as high inflation caused a run on gold. Rather than raise taxes to pay for spending, the U.S. left the Gold Standard. e. Token money, coins, have little intrinsic value. 7. Types of money has more information 8. Does Gresham's Law applies to people as bad economic times causes people to leave an area making those remaining, on average, less able to compete.
D. The Demand for Money
Review Types of money are M1 cashDD are only backed by faith M2 are Near moneys like savings accounts and treasury bonds B3 M2 plus time deposits $100,000
|
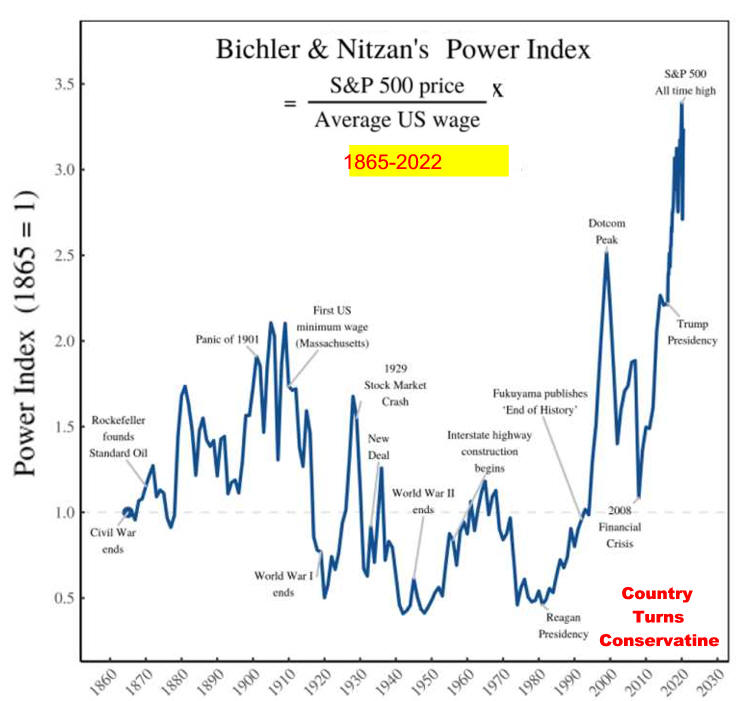
Political Economy
Gresham's Law
|
|
III. US Private Banking System A. Three kinds of banks 1. Commercial banks offer demand deposits (checking accounts)
2.
Savings and loan associations used to specialize in time deposits commercial banks. B. Federal deregulation contributed to banking difficulties in the 1980's. C. Visit brief
history provided
by the Federal Reserve Bank for D. A Concise History of US Banking from Quick Notes A . Board of Governors oversee the Federal Reserve System 1. Seven governors 2. Governors are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. 3. The chair is appointed by the President for a four-year term. a) To foster independence, term does not coincide with President's term. b) Other board members are appointed to 14-year terms on a staggered basis to insure an experienced board. c) Understand Political Economy using the FED and financial market videos 1) The Man Who Knew: The Life and Times of Alan Greenspan 45 2) More Money Than God: Hedge Funds and the Making of a New Elite 58 3) Niall Ferguson: Financial Crises, Populist Backlashes, Lessons of History 82 d) Who Owns the FED e) Is political-influence appropriate |
Districts
|
|
Unit IV. Summary
FED is a somewhat private-sector entities
V.
Functions and History of the FED |
The Federal Reserve System
Expanded Operations Chart
|
|
Federal Open Market Committee meeting at the Federal Reserve in Washington, DC |
|
B.
FED Powell's Annotated Press Conference 4/29/20 C. The Fed's Coronavirus Response in Historical Perspective
D. History
Unit V. Review Functions
VI. Fractional Reserve System/Creation of Money
VII. The Monetary Multiplier
Unit VII. Review
Monetary multiplayer measures the
|
History Readings 1. How we learned to stop worrying and embrace the abstraction 2. 300 Years-of-financial-crises-1620-1920 4. The continental currency crisis of 1779 and today's European debt crisis 4/11/14 5. Central bank crisis management during wall street's first crash in 1792 5//14 6. The Slump that Shaped Modern Finance 4/14 7. Infographic History of U.S. Money 8. History of the Gold Standard 10. A Brief History of U S Banking Problems and
11.
The Essence of Money, a Medieval Tale
(7:36)
Stay Current With
Global Economic Intersection Newsletter Economy Continues to Grow Modestly Yellen Says the Economy is Growing Moderately
Source and prediction of coming inflation A. Laffer, 6/11/14
|
|
VIII. Recent Developments
2.
Consolidation has caused their numbers to decline and their
3. Many
bank/thrift services are now performed by insurance
4.
Rise of the Shadow-Banking System 2. Congress Is Politicizing the Fed Jan 25, 2010
3.
Central bank independence versus inflation 6. Money, Banking and the Federal Reserve 43 min conservative video
7.
Central Bank Independence: Growing Threats
1/2/17 |
Source and prediction of coming inflation A. Laffer, 6/11/14
|
|
IX.
Additional reading
Source The Economist 4/5/14
Editor's Note: How much of recent
price stability is the FED and How much is world-wide competition.? |
Other Macro Chapters |
|
X.
Twentieth Century U.S. Political
Economy is About Money Source A Concise History of U.S. Banking  Leading
monetary economists of the 20th century Leading
monetary economists of the 20th century
Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz authored the classic A Monetary History of the United States
The 19th Century ended
with
Monarchs in control and liberal economic thought expanding. Interesting Studies
Editor's Note:
|
 |
|
Last
Chapter
|
|
 Facts On The Early History Of The US Dollar
|
|
|
|
|



|
XI. Visual Learning Stuff.
source econintersect.com/ Some Central Banks Are Easing to
from http://www.ritholtz.com/blog/2013/04/mid-week-pm-reads-15/
Source econintersect.com 2014/09/28/
|
g