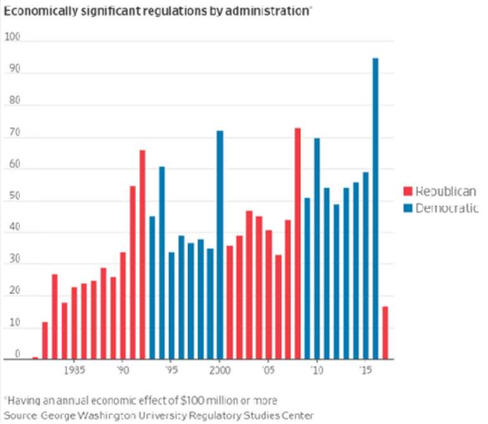
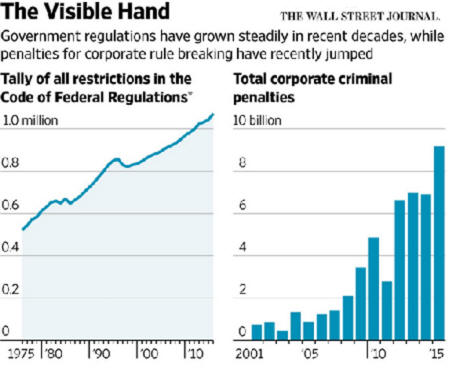
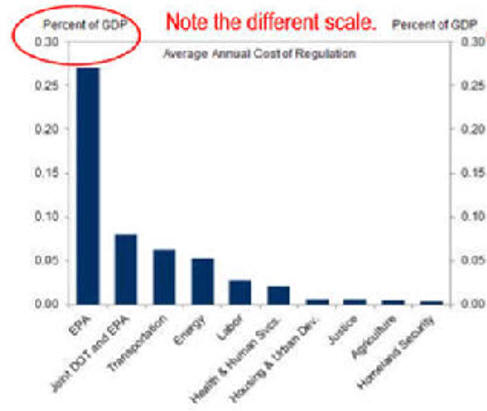
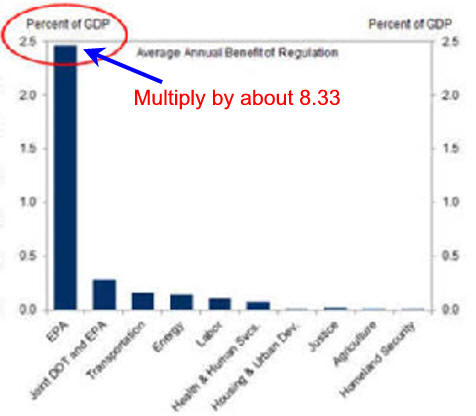
|
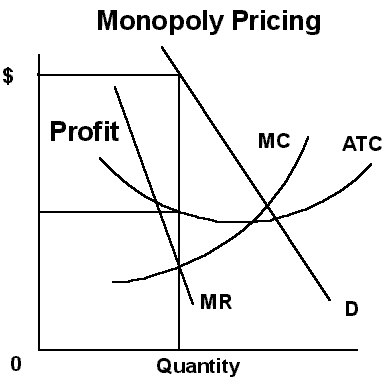
IV. Antitrust
prosecutions
A. Enforced by the antitrust division of the
Justice Department
B.
THEODORE ROOSEVELT
took on the corporate monopoly
Trusts that control
railroad rates and routes and thus destroyed
small towns and
farms
C.
Rule of Reason
1. Applied by the Supreme
Court in a 1911 antitrust case
against Standard Oil of New Jersey and the American
Tobacco Company
2. Court stated that
behavior must be unreasonable in a competitive
sense and anti-competitive effects must be demonstrated.
3. Both companies were
found guilty.
4. The Court ruled that
bigness alone was not against the law in
1921 when it ruled that U.S. Steel was not a monopoly even
though it controlled 50% of the market.
5. Bigness alone was
prosecuted by the Supreme Court in 1945
as it broke up Alcoa
because it controlled 90% of the aluminum
market.
D. Tight enforcement, which began
in 1914, ended in the early 1980's.
E.
For more information read
1.
Rule of reason
- Wiki
2.
Executive Summary Of The Anti Trust
Laws
F.
Videos
1.
No Recent Prosecution of Financial Fraud
2.
Reinstating Glass-Steagall
V. Internet Readings
A.
The Great Recession
was aided by poor government regulation. 12/27/14
B.
Who Makes the Rules 4/13
Economics Intersection
C.
Democratic
Capitalism vs. Capitalistic Democracy
D.
Documentary-of-the-week-FINRA- Madoff history video
E.
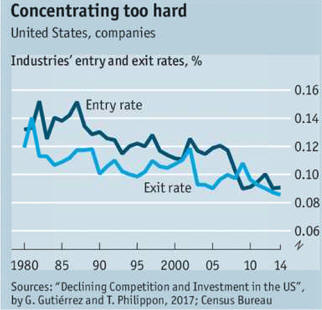
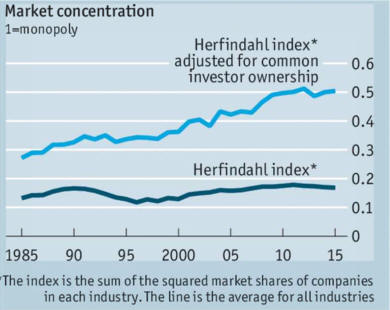
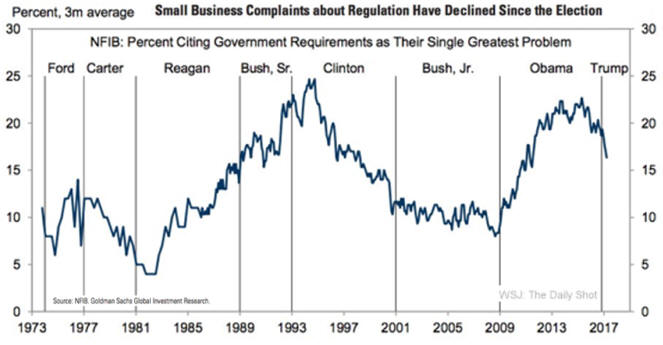
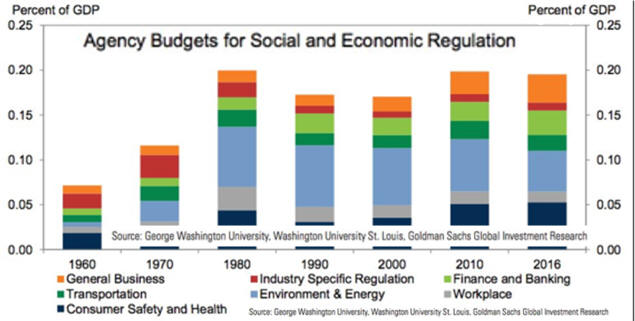
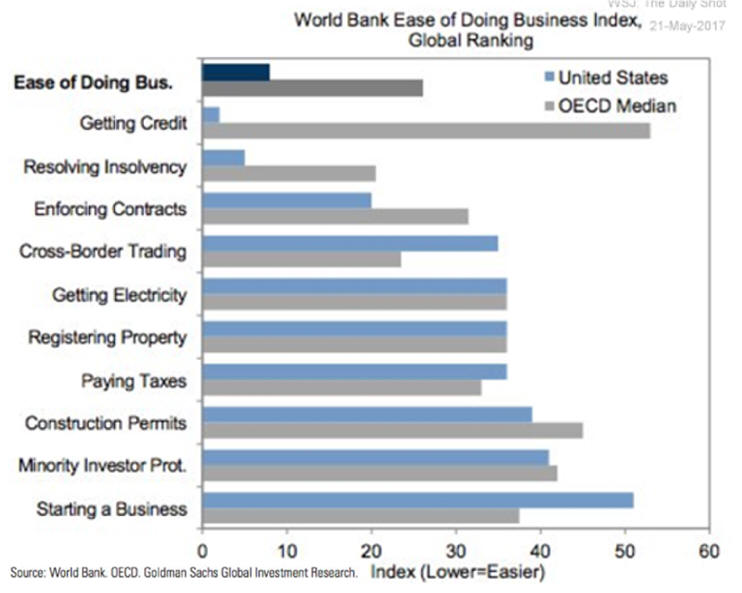
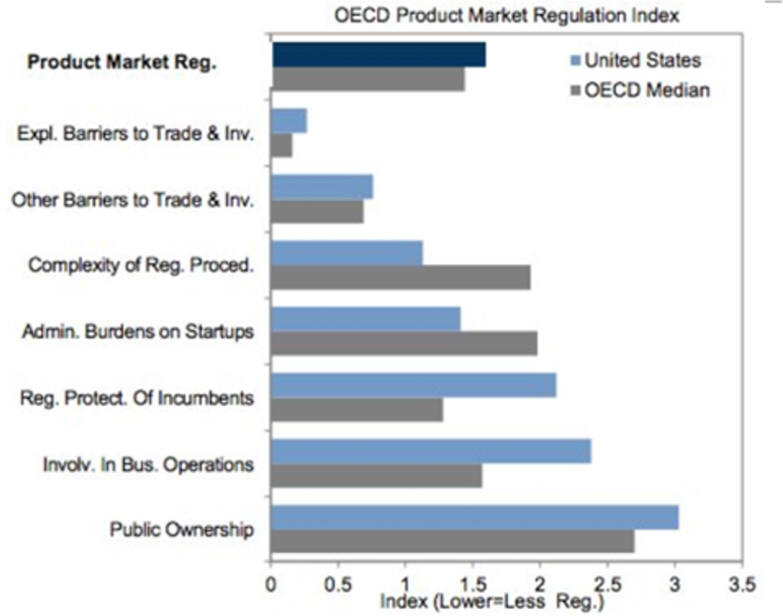
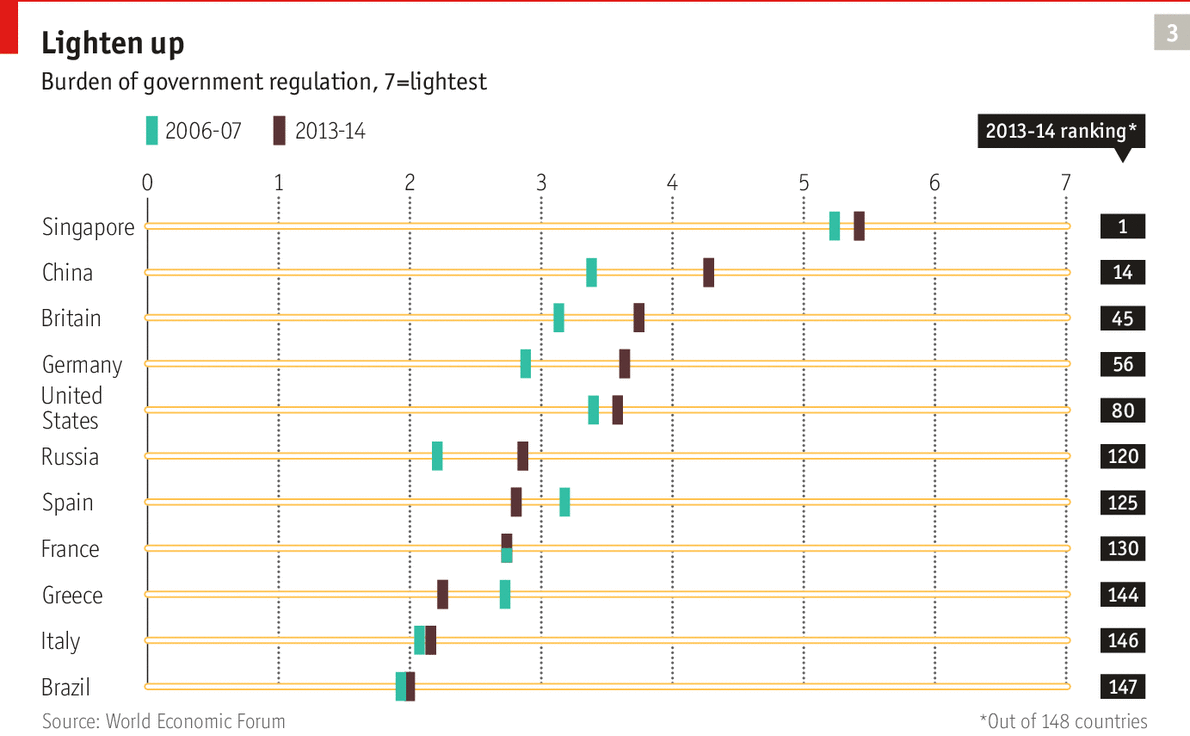
Rich world needs to cut red-tape and encourage business 2/22/14
See chart
F.
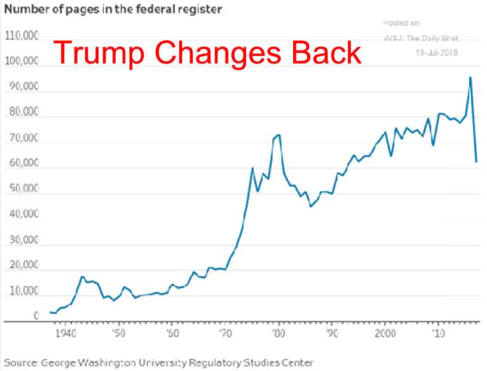
Why Regulation Goes Astray
5/21/14
G.
Economic Normality1945-2015 |

Ida
Tarbell and other
investigative
journalists were called
Muckrakers.
She exposed
Standard
Oil Trust. Working for
McClure
Magazine and other monthly magazines they help educated the public
from 1890 to 1929 in what is known as the
Progressive Era.
Books also help the education process.
The Jungle
exposure of health violations and unsanitary practices in the
early 20th century American meatpacking industry.
The Octopus
exposed a large interlocking network of
criminal conspiracy that reaches into every part of the U.S.
government, other national governments, and most of sector's of societies.
The
Bitter Cry of Children exposed the terrible child working conditions.
Some tried night school but after working ten hours learning to read was
difficult.
Business Progressivism of the 1920's typified by Henry Ford and
Herbert Hoover
put an emphasis on efficiency.
As of 2018, at least 18 states have enacted joint-employer
shield laws specifically designed to protect one very wealthy special
interest group: corporate franchisers. Corporate
franchisers are the big companies—like McDonalds, or Marriott, or Carl’s
Junior—t These state joint-employer laws are intended to shield the
corporate owners of the franchise from bearing joint responsibility with
their franchisees for complying with minimum wage, overtime, health and
safety, and other laws applicable to the employees who work at the
franchisee’s stores. In simple terms, the joint-employer shield laws
preclude applying the joint-employer legal doctrine to hold franchisers
jointly responsible for violations of employee rights.
What states have joint-employer shield laws?
The 18 states as of January 2018 are Alabama, Arizona,
Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, New Hampshire,
North Carolina, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas,
Utah, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
|