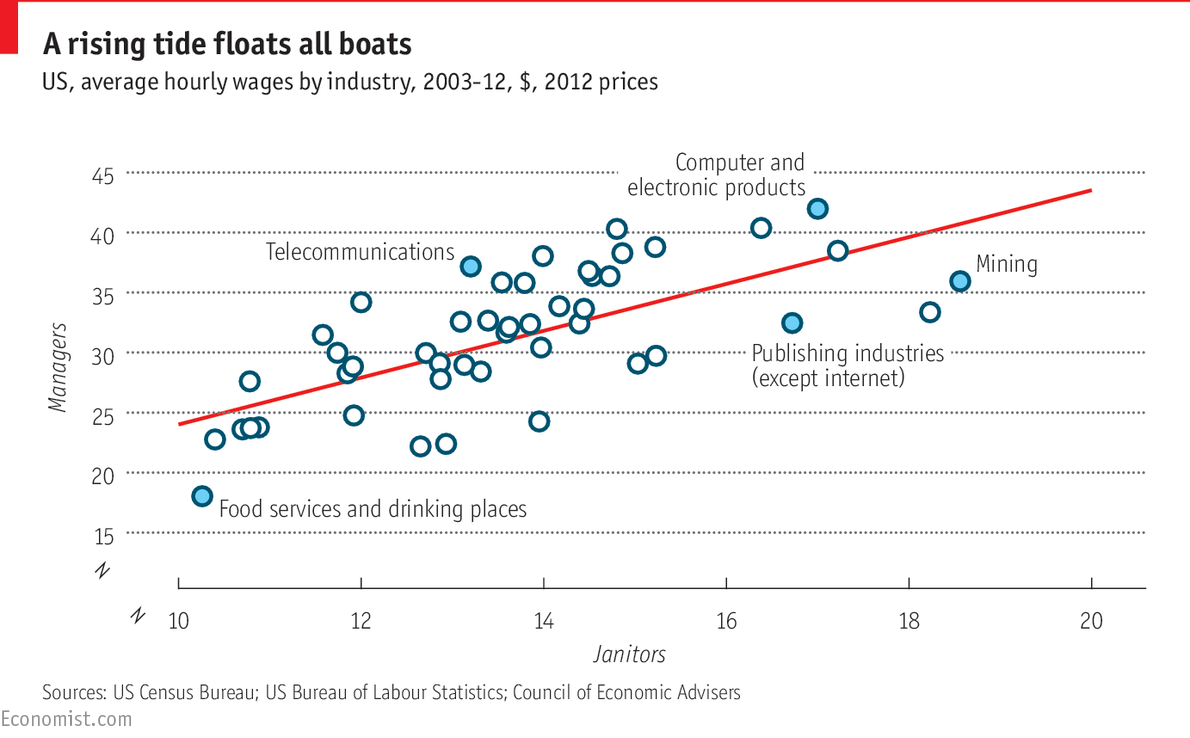
|
Lecture Notes
One-page printable
I. Overview
A. A purely competitive market exists when
the number of independently acting buyers and sellers
is so large that individual participants have no affect on
market price and quantity.
B. Products sold are virtually identical. Agricultural products such as potatoes and wheat
are examples of competitively sold products.
C. Pure competition industries as defined is difficult to find because some
monopoly power usually exists.
D. Price is determined by intersection of industry supply and
demand.
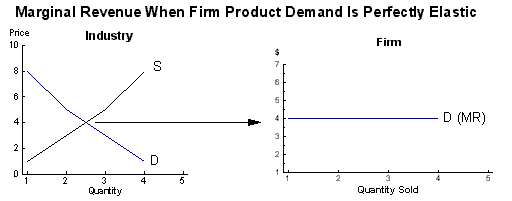
E. Individual firms are
Price
Takers as they inherit a horizontal
demand-marginal revenue curve from
their industry.
1. A firm can not sell above market as products
are identical and no one will buy higher than
market.
2. There is no reason to sell below market
as it would
mean less revenue and less profit.
Unit I. Review PC requires many independent competitors
selling virtually identical products.
From
chapter 22 on Understanding
Profit
II. Purely Competitive Adjustment
A. Suppose industry demand and
supply yield an equilibrium price P at which a firm's
economic profit is zero.
1. Step 1
An increase
in
demand to D' causing
economic
profit.
2. Step 2
Market entry is relatively easy increasing industry
economic
profit draws in new firms
increasing
supply to S', lowering and economic
profit disappears.
3. This automatic
purely competitive adjustment causes long-term economic profit
for pure competition
move toward zero.
4. Many feel a zero long run
economic profit represents an ideal economic model
as all the company earns is a normal return on
investment.
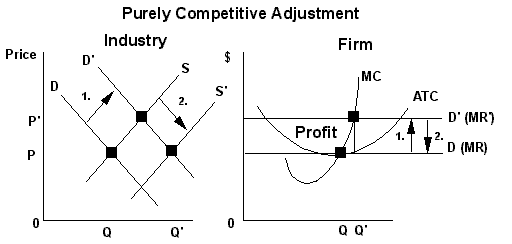
Review Price equal ATC where MR = MC with no profit
B. Suppose a Purely
Competitive Company Makes a Profit
1. Price is higher than average total cost so total
is greater than total
cost.
2. Cost includes a reasonable return on investment called
"normal profit"
so under this definition of cost, any profit is an excess.
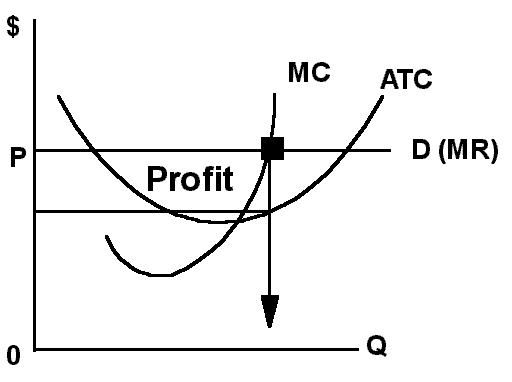
Review PC making a profit doesn't last
long a people see the abnormal profit and try to get some.
|
Please Visit
Economics Internet Library
Political Economy
Stuff

Examples
1.
Post WW2 International Economic Competitive Adjustment
2. Mark Blyth:
Competitive Adjustment in
European Market Area at 1 min
3.
Competitive Adjustment Applied to Trumpism
begins at 4 min 15 sec
Competition in the Grocery Business,
Finance-Not-So-Much

Source
U.S. Economic Growth Over?
from
economist.com
Videos
1.Profit
Maximization for a Competitive Firm
D. Kaufman Wisconsin-Parkside.
2.
Profit Maximization in Perfect Competition
F. MacLauchlan
3.
Perfect Competition Graphing Practice Econ in 60
seconds
3.
Perfect Competition in the Long Run from Econ in 60
seconds 4. Market
Equilibrium in the Long Run from Dennis
Kaufman Wisconsin-Parkside
5.
An Invisible hand
provided by
competition, regulates the market. |