|
|
|
Index Prelude: Polarity in America 1. Wellbeing: Government Income Inequality Stagnate Wages 2. Measuring: Inflation Employment Failure of Capitalism3. Macro: GDP Usefulness Distributing GDP Growing GDP4. Micro: Most Westerners Live Better Than Ever 5. Western Political Economy Post WW 2 US Competitive Adjustments Post WW 2 International Economic Adjustments Western European Political Economy Source has active links Polarity in America:
|












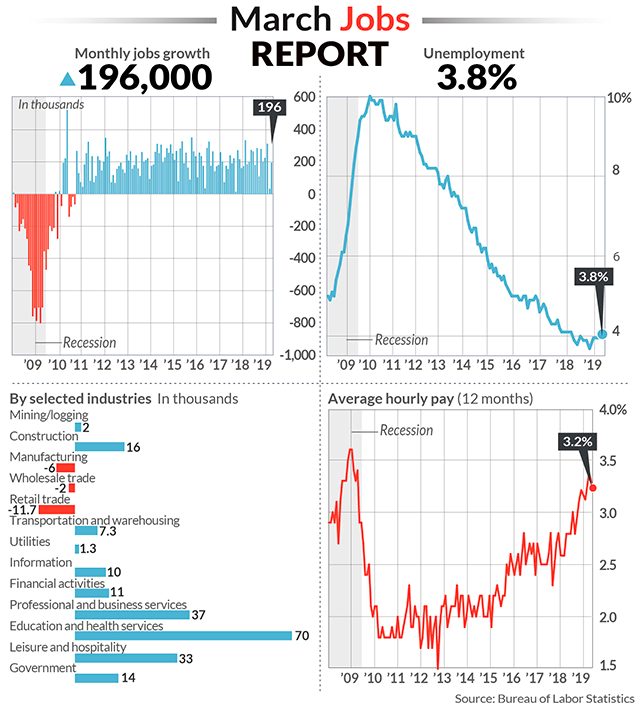








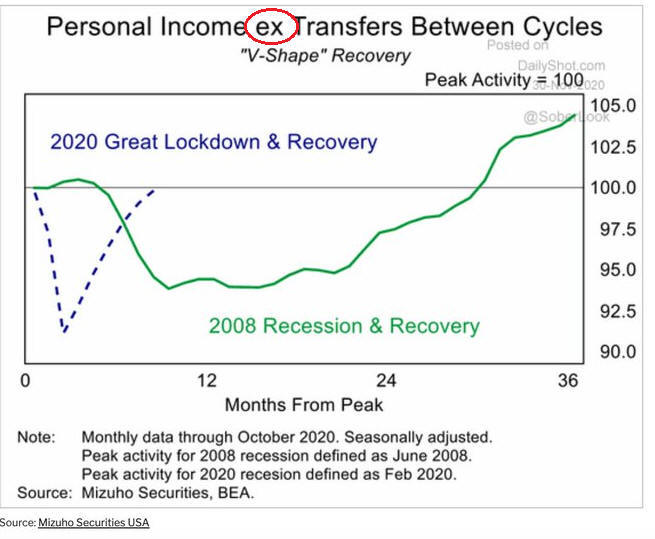
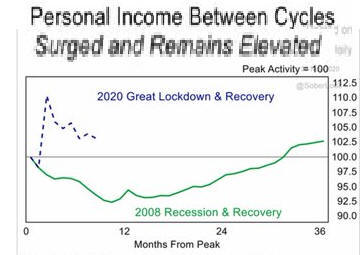
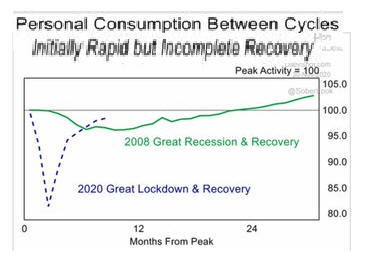





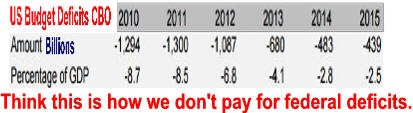

 New Normal # 6
Profit
Beating Labor Twenty-first century war expenditures helped profit recover after a
New Normal # 6
Profit
Beating Labor Twenty-first century war expenditures helped profit recover after a