|
U.S. Economic Normality 1946-2015 2. The Economics 3. Presidential Politics 4. Supreme Court
|
|
Prelude Cuban Missile Crisis continued a long Cold War. Party Control Flip Flops Like a Yoyo but Progress Is Being Made. Republicans were penalized by outrage caused during the summer of 1932 because of Veteran Bonus Army deaths. It combined with the of Hoover's domestic policies and change was demanded. A similar major change happened with Reagonomics, See Liberal Richard Wolff's Video On Reaganomics Democrats promoted American Liberalism. It anchored in a coalition of specific liberal groups, especially ethno-religious constituencies (Catholics, Jews, African Americans). White Southerners, well-organized labor unions, urban political machines, progressive intellectuals, and populist farm groups were also courted. |
The Economics
Post WW II Activity Included
Reorganization of Israel
resulted in a strong pro-American Middle East democracy.
Federal Aid Highway Act
created interstate highway system for
national defense purposes and allowed the development of
suburbia.
Environmental Protection Agency was created by presidential
executive order. It along with the
Clean Air Act Amendment of 1990 increased federal regulatory
authority. 26th Amendment of 1971 lowered voting age
to18
Americans with Disabilities Act of
1990...
Bailouts began
1975 New York City
$1.3b
paid back +interest 1979 Chrysler Motors
$1.5b
paid back +interest 1982 Oklahoma-based Penn Square Bank $65m
1984 Continental
Illinois Bank
bailout $14b 1980's Savings and Loan $124.6b [2] 4. Less Regulation Causes Trouble Financial deregulation began in early 1970's and culminated with Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act of 1999 which repealed the Glass–Steagall Act enacted after the Great Depression. Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000 minimized regulation of financial derivatives |
War The three year Korean War killed 36,574 with 103,284 wounded in action. South Korea remained free. Japan felt safe and used a small defense budget to build industrial capital and rejoined the developed world. The very long Vietnam War2 killed 58,220 with over 153,303 wounded with few important positive results. As of 12/31/14 Afghanistan War killed 2,312 with 20,026 wounded with few important positive results. As of 5/29/12 Iraq War killed 4,425 with 32,223 wounded with few important positive results.
|
|
| Republicans | Democrats |
| Presidential Elections |
"And Now the Rest of the Story |
|
Election of 1948 was a major upset as H.S.Truman fooled the pollsters when his whistle stop strategy proved personality had defeated New York Governor John Dewey's political machine. |
Harry S. Truman, a product of the Kansas City Old boy network, made these difficult decisions 1) used "the bomb" to quickly end WW2, 2) quickly recognized the new State of Israel 3) used the Marshall Plan & NATO to prevent a repeat of post WW I type international problems 4) officially ended Monroe Doctrine isolationism with the Truman Doctrine and 5) he relieved from duty popular war hero General Douglas MacArthur who had trouble following Korean War presidential instructions. |
|
Election of 1952 Winning Republican candidate Eisenhower had
been courted by Democrats. He campaigned against the Truman policies he labeled
as "Korea, Communism and Corruption."
Election 1956 saw a popular unhealthy president easily win the last 48 state election. Ike was the last presidential candidate born in the 19th century . |
Dwight D. Eisenhower quickly ended the Korean War but by helping England's Churchill overthrow the democratically elected Iranian government; he extended U.S. the Middle-East involvement. His accomplishments include enhanced national security with the 1956 Federal Aid Highway Act and increased Patriotism accomplished by making faith a more important part of American politics. Upon leaving office he warned of dangers from the military industrial complex. |
| Election of 1960 saw Kennedy win by only 112,827 votes though the Electoral College vote was 303 to 219. Nixon was the first loser to win the state battle 26 to 23 while Alabama and Mississippi went for Harry F. Byrd. Oklahoma's "faithless electors" accounted for the missing state. The election of two incumbent U.S. senators (Kennedy and Johnson) was a first that would not be repeated until 2008. | John F. Kennedy Our first Roman Catholic president began with poor execution of the Eisenhower designed and Nixon planned Bay of Pigs Invasion. Many conservatives feel he should have drawn a RED LINE in relation to the 1961 Soviet inspired Berlin Wall crisis. Among his major accomplishments during his assassination shortened presidency were the 1963 Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, the Peace Corps, the Space Race to land an American on the moon and some Civil Rights progress. |
| Election of 1964 saw an unsuccessful bid from Republican conservative Senator Barry Goldwater but his ideas influenced the modern conservative movement and began a long Republican Party realignment. | Lyndon B, Johnson was a master politician who put aside animosity from most Kennedys and ushered through congress the 1965 Social Security Amendments which created Medicare and Medicaid. The Voting Rights Act of 1965 began a long-delayed national healing process existing from long before the Civil War. Many feel Johnson's unpopular Vietnam War escalation made for an unhappy end to his presidency. |
|
Election of 1968 was a major
realigning election as it permanently disrupted the
New Deal Coalition that had dominated presidential politics
for 36 years. It centered on restoring
law and order to a country torn by riots and crime. A
wrenching 1968 campaign was conducted during violence that included
the
assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. and subsequent
race riots plus the
assassination of Democratic presidential candidate Robert F.
Kennedy. Nixon just beat
Hubert Humphrey in the popular vote but easily won the
Electoral College while third party candidate
George Wallace
got almost ten million votes for the far-right
American Independent Party. Election of 1972 was an easy Nixon victory as Senator McGovern's anti-war campaign was hurt by his outsider status, limited party support, perception he was a left-wing extremist and a V.P. nominee T. Eagleton scandal. |
Richard M. Nixon was
possibly our most
contentious
president.
He accomplished a nuclear arms control agreements with the Soviet
Union, instituted successful diplomatic relations with China and the
Nixon
Doctrine began the long process of ending the Cold War.
Domestically he enforced
desegregation, established the
Environmental Protection Agency and tried but failed to
control inflation with wage and price controls.
His desire to maintain U.S. international
credibility by extending U.S. Vietnam War involvement
eliminated any possibility that liberals would ignore the
Watergate Scandal
and he was
impeached. Gerald Ford probably doomed his political future with a quick Nixon pardon. Ford lived longer than any other U.S. president, 93 years and 165 days and his 895-day presidency remains the shortest term of all presidents who did not die in office. |
|
Election of 1976 Ford who was not able to secure the nomination over R. Reagan until the Party Convention lost to relatively unknown former Georgia Governor J. Carter. Carter's narrow victory made him the first president elected from the Deep South since Zachary Taylor in 1848. |
Jimmy Carter's 1978 Camp David Accords were the high point of recent Middle East peace efforts. Carter inherited stagflation. The inflation part was solved with the pain of two recessions orchestrated by his FED Chairperson Paul Volker. Economic growth had to wait until after Ronald Regan tax cuts/deficits. |
|
Election of 1980 saw Carter attacked Reagan as a dangerous right-wing radical while Reagan won easily as he pledged to uplift the nation's pessimistic mood. Congressional elections also went Republicans for the first time in 28 years. This began the Reagan Revolution which signified a conservative national political realignment. Election 1984 went Republican as the economic stagflation of low growth with high inflation was over. Reagan joined Nixon (1972) as the only candidate to carry 49 of the 50 states. |
Ronald Reagan cut taxes, increased defense spending, ignored federal deficits which today look insignificant because of nominal economic growth. His Supply Side Economics sought economic growth through more efficient production caused by less regulation and low taxes rather than government supported demand. His low taxes and large military spending was Keynesian demand supported growth that soon lowered the relative size of the annual federal deficit and accumulated debt. The later had stayed below 40% of GDP until 1) New Deal and 2) WW2 spending caused it to peak at 120% of GDP. The Penn Square 1982 Bank bailout began a new chapter in the long history of government helping business. |
|
Election of 1988 saw a good economy, a stable international stage, and Reagan's popularity foster the third consecutive presidential victory for the Republican Party. It was the first time that a party had won more than two consecutive presidential elections since the Democrats won five straight elections from 1932-1938. |
George H. W. Bush popularity peaked early because his 1990 Coalition of the First Gulf War repelled Iraq's Kuwait invasion. Not always conservative, he signed the Immigration Act of 1990 that led to a 40 percent increase in legal immigration and his temporary ban on certain important semiautomatic rifles cost him a NRA endorsement. |
|
Election 1992 went to Clinton as 1) Bush broke his
no new taxes pledge, 2) the economy was in
recession 3) Bush's perceived foreign
policy strength was less important with the fall of the Soviet Union
and Middle East stability after the Gulf War victory. Economic
conservative Ross Perrot got 19% of the vote helping Democrat Clinton.
|
Bill Clinton was another contentious president who survived the Lewinsky scandal as twenty-five years of increased education had cultivated a mare tolerant nation. This allowed him to appoint more women and minority federal court judges than white male judges and also to have a very diverse cabinet. The longest economic expansion in American history allowed for increase educational opportunities, lower crime and increased homeownership. The little noticed 1999 Gramm, Leach, Bliley Act initiated by Republicans and signed Democrat Clinton continued Republican liberalized of financial regulation which added to the many causes of The Great Recession. |
|
Election of 2000 was one of the most contentious in history
as it marked
the fourth time the winner failed to win a plurality.
See
1824,
1876, and
1888). A
Florida recount required Supreme Court intervention which followed
party lines. The
Green Party adversely affected Democratic
Al Gore. |
George W. Bush reacted to
September 9/11 attacks with a
War on Terror,
a
War in Afghanistan and the
Iraq War.
His major tool was the USA PATRIOT Act which established Department of Homeland Security. He
also implemented
1)
tax cuts 2)
No Child Left Behind
3) Medicare Part D but vetoed State Children's Health
Insurance Program legislation 4)
government activities to
|
Supreme Court
Sovereignty of Federal Government Over Sates Governments
1949 Wolf v. Colorado unreasonable search and seizure.” allowed in state court enforcing state law reversed 12/17/54
1954 Brown v. Board of Education see Helped Spark the Civil Rights Movement videos
1958 Crooker v. California limited right to counsel before trial creating Miranda rights reversed 6/13/66
1973 Roe v. Wade created a national law concerning abortion reversed 6/26/22
Supreme Court as "Supreme Constitutional Authority"
1962 Baker v. Carr federal courts took control constitutionality of state redistricting plans.
Other 1960's Redistricting Decisions
Protecting Business
1990 Austin v. Michigan Chamber of Commerce allowed state law to ban corporate political contribution reversed 2010
2010 Citizens United v. FEC protected corporate interests in election-spending regulations
The Economics
|
#1 Rising Income
Normality ended when Carter appointee FED Chairman Volker found higher
interest rates were not enough so he lowered commercial bank
reserves. This quickly pushed the Federal Funds Rate to 20%. Banks would not loan. Two recessions followed. The first cost
Carter
reelection and the second, though severe, was over so Reagan was
reelected.
|
|
#2 Increased Foreign Competition
Began 1970's Wage Stagnation
|
|
#3
1980's Failing Manufacturing
and Less Financial
Regulation Events Causing Financial Instability Causes Great Recession 1980's U.S. and England Returned to Conservative Lax Business Regulation because increased regulation and increased welfare provisions had upset many voters. Think Great Society and lax derivative regulation which result in major increases hostile leveraged buyouts plus and over-investing in Real estate caused. They caused the Savings and Loan Crisis. Think Michael Milken Scandal, Keating Five results from poor Alan Greenspan advise. 1980's Major Investments Banks Went Public creating a need to balance client needs with equity needs. Think expansion of financial industry's share of GDP. 1980's Accounting Standards Declined as accountancy firms struggled to balance commitments to audit standards with the desire to grow their consultancy business. Think off-balance-sheet items and Arthur Anderson Scandal. 1980's Home Equity Loans Increased Current Consumption and Lowered Savings as they replaced equity building home improvement loans. Think many not prepared for retirement. 1983 Reverse Mortgages Approved for FHA loans. Think less retirement savings. 1986 Big Bang deregulates London's financial services industry, other will follow. 1999 Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act Increased Systemic Financial Risk once limited by the Glass-Steagall Great Depression Act. Initiated by Republicans it was signed by President Clinton. Think financial industry expansion. See Five Bad Bush/Clinton Policies 2004 Uptick Short Rule of 1938 rescinded. Think stock market gambling. 2006 FASB requirement that housing assets be mark-to-market decreased financial system collateral. Action resulted from a 1991 Government Accountability Office investigation of the $160,000,000,000 savings and loan bailout. Think moral hazard.
From Financial Crisis to
Recession to Great Recession to Recovery
Understanding Balance Sheet Recessions
|


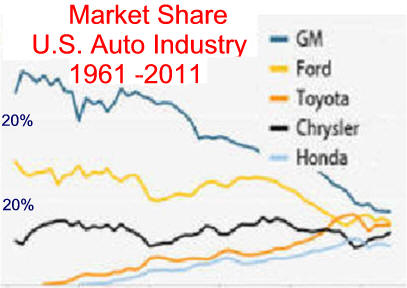
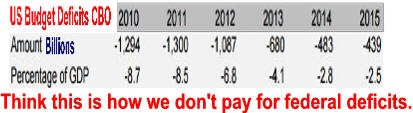 Bailout History
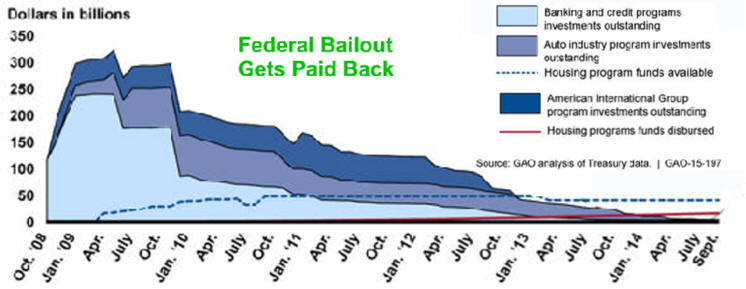
The $700 billion 2008
financial-sector rescue plan is the latest of many bailouts that go
back
to the
Bailout History
The $700 billion 2008
financial-sector rescue plan is the latest of many bailouts that go
back
to the
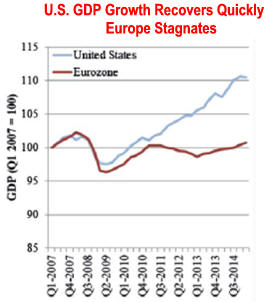

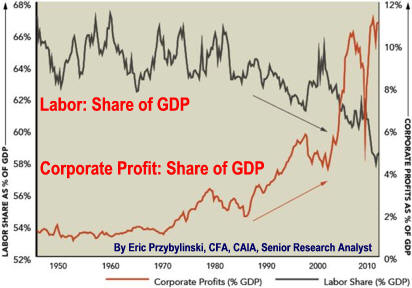

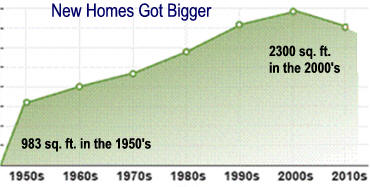 3) Personal Income increased continuously if not always rapidly
because nature and nurture improved the personal characteristics
needed to enhance wellbeing.
Think Russia, China, and
Europe's really slow recovery from the Great Recession. Source
3) Personal Income increased continuously if not always rapidly
because nature and nurture improved the personal characteristics
needed to enhance wellbeing.
Think Russia, China, and
Europe's really slow recovery from the Great Recession. Source
