|
#12.
1800 Sees First Peaceful Democratic Power Transfer
Republican ideology of the late 18th century
believed political parties were
detrimental to society because they served vested interests. A nonpartisan
elite would best served the Republic but differences and party politics
developed. Thomas Pain wondered if Washington was a traitor or an
imposter. Federalist Adams won the 1796 election and the constitution indicated
second place finisher Jefferson was Vice President. The two friends had
different political beliefs and would not get along .A key differences between the two was diplomatic
relations with England and France. Federalist loved Britan and idealized
their government. They felt the U.S. was too weak to get involved with
the intense war between the two countries. They also hated the French
because of the anarchy that had resulted after the French Revolution.
Jefferson's group had strong Republican beliefs and soon were called Republicans. They felt the Federalist wanted to turn the fledgling Republic into a Monarchy plus and they wanted to help revolutionary
war ally
France.
Federalist believed in a strong central government
as demonstrated by the Washington administration assuming state
revolutionary war debt even though some states had already paid their
debt. They also formed the Bank of the U.S and generated
revenue with a new tariff. Both helped the Northeast industry much more
than Southern agriculture.
Republicans lived in mostly rural states. They felt these actions
endangered the Republic. They wanted a weak central government that did
not need revenue and they didn't like the eastern bankers or their
tariffs. They wanted states rights.
Source |
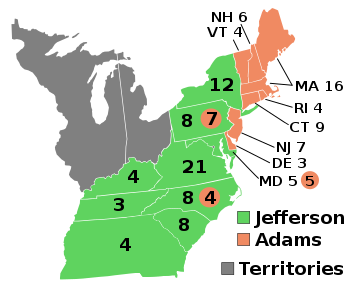
The 1800
Presidential Election was very
rancorous
because no rules
of acceptable behavior existed and politics could be a messy business. The Aurora of Philadelphia
became the mouthpiece of the Jeffersonian Republicans.
They
printed that Adams was a Monarchist who would
appoint himself King. His son would be the
hereditary successor. They said Adams had ordered a
boatload of prostates delivered from England to meat
his lustful passions. The Porcupine Gazette did the
same for the Federalists. They printed Jefferson was
an atheist and anarchists. Two mistakes hurt Adams. In 1798 he
had created a standing army
and enlarged the Navy. This hurt because traditional
Republican orthodoxy preached that a standing army
always led to a dictator. A
citizen soldier was enough to meet emergencies.
Second, the Alien and Sedition Acts hurt on two fronts. Immigrants didn't like the Alien Act which made them
wait longer for citizenship and allowed them to be
arrested and even deported. The Sedition Act made
Republican written anti- government literature illegal. This
would be the first of many such instances where the
President's would abuse the Constitution in the name
of national security. The election ended in an
Electoral College tie. Receiving votes were two
Federalists , Adams( 65) and Thomas
Pickney(64) plus two Republicans Jefferson(73) and
Aaron Burr(73), John Jay had one vote. The election
went to the House of Representing. Hamilton worked
behind the scenes for Jefferson who he felt
was
less-dangerous than Burr. The runoff was tied for 36 ballots
and finally on number 37 Jefferson was declared the
winner. The U.S. became
the first society to followed a revolution with a
peacefully transfer of power.
In his Inaugural Jefferson said "We are all
Federalists, We are all Republicans." This assured a
more peaceful power transfers. Two interesting side-note. VP Burr later killed former
Treasury Secretary Hamilton in a dual. Former
friends Adams and Jefferson became bitter enemies
because of partisan
politics and didn't communicate until 1812
when letters between the two healed the damage.
Letters continued until their death on the same day
of 7/4/26, the 50th anniversary of the
nation's birth. |

Federalist and Republican
House quarrel.
Foreign
influence on Domestic Politics
|