|
Market System Participants
Chapter
7
A. Households
(families and individuals)
receive income in return for their
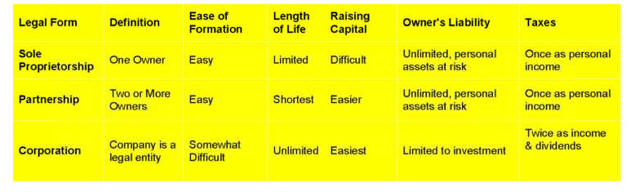
B. Businesses
C. Federal government
1. Government spending has grown because of
a. Population growth b. War and defense requirements
c. Urbanization d. Environmental concerns e. Inflation
f. Transfer payments
1. Social Security
2. Medicare and Medicaid 3. Terrorism
4. Social programs:
Aid to Families with Dependent Children
5. Mid-1960's
were 3% of national output, today they are
12% of
output
2. Government spending and taxing
a. Federal spending and taxing
1. Expenditures
a. Income security b. Defense (military preparedness)
c. Interest on public debt
d. Discretionary programs
2. Receipts
a. Personal income taxes
1. Marginal rate is the rate paid on
additional or
incremental income.
a) The increase in taxes paid divided by the
increase in
income.
b) In a progressive tax system, each higher tax
bracket (grouping) has a
higher rate on the
income in the higher bracket.
2. Average tax rate is the taxes paid
divided by total
taxable income.
b. Payroll Taxes: premiums paid on compulsory
insurance plans
1. social security and Medicare (both employer and
employee pay)
2. unemployment taxes (just employer pays)
c. Corporate Income Taxes
d. Excise Taxes are a sales tax on items such as
jewelry, tobacco, and liquor.
e. Licenses and Fees
D.
State and local
governments
have mandatory balanced budget
laws making the accumulation of
debt difficult
|
E. Taxation philosophies
1. Ability to pay is on people with
high income or
wealth.
a. Income tax
b. Sales tax c. Estate taxes
2. Benefit received
(User taxes)
a.
Those who derive a benefit
pay for said activity.
b.
Examples
1. Gasoline taxes are used to improve roads.
2. Social security taxes are used to provide
retirement and
other benefits for participants.
F. Taxation philosophies
1. Ability to pay
a.
Those with the ability (income or wealth), pay more.
b.
Examples
1. Income tax
2. Sales tax 3. Estate taxes
2. Benefit received
(User taxes)
a.
Those who derive a benefit from some government action
pay for said activity.
b.
Examples
1. Gasoline taxes are used to improve roads.
2. Social security taxes are used to provide retirement and
other benefits for participants.
G. Types of tax rates
1. Progressive
a.
Tax rate increases as income increases
b.
Tax rate decreases as income decreases
c.
Those earning higher income pay a higher average tax rate.
d.
Example: Federal Income Tax
Note: Moving into a higher tax bracket does not result
in your paying a
higher rate on lower bracket earnings.
2. Proportional
a.
Tax rate as percentage stays the same.
b.
Examples: Social Security taxes are proportional up to the maximum income
level of about $76,200 because both employer and employee pay a constant
rate of about 8%, but then
the tax is
regressive as the rate drops to zero
3. Regressive
a.
Amount paid divided by income drops as income increases.
b.
Happens one of two ways
1. Rate drops as income increases (FICA after about $76,200 in
2000)
2. Amount of tax is constant so at higher incomes, the effective tax rate
is
lower (excise taxes on cigarettes, liquor, etc.)
H. Shifting the tax incidence
. 1. Passing the burden of taxes onto others (consumers ultimately pay)
2.
Businesses and professionals try to do this
3. The
consumer bears most of the tax burden in a market econom |