Rent Interest Profits Chapter 29
Economic rent
A. applies to amounts above those required
to keep factors
employed at
their current use, i.e., the factors' opportunity cost.
1. Since economists include a
normal return on investment in costs,
any
profit represents rent, a surplus.
2. Companies with monopoly
power that results in profit receive economic rent.
B. Pure economic rent is the concept of economic rent applied
to
factors fixed in supply such as
land and other natural resources.
C. Economic implications of pure economic rent
1. Supply is fixed, perfectly
inelastic, and price therefore does not
perform the
incentive function of increasing quantity supplied.
2. Socialist philosophers questioned
whether pure economic rent should be paid.
a. Originally
free, owners of land receive pure economic rent which is a surplus.
b. Henry
George wanted to tax rent away in 19th century America.
1) Called the single-tax movement, he wanted to replace
all taxes with one tax on land.
2)
Three problems exist with this philosophy.
a)
Land is not free to current owners.
b)
Capital improvements are necessary to make modern land useful.
c)
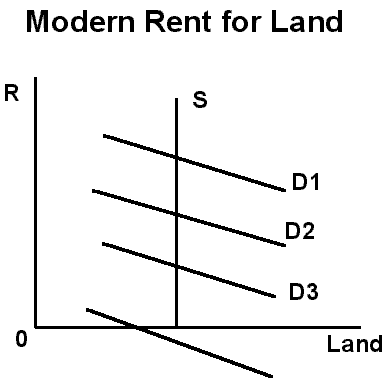
Modern rent does perform a rationing function because land is of such differing
quality.

Interest is the price paid for capital
A. The price of capital goods (any person-made aid to
production)
will be analyzed.
B. Our main concern will be the cost of the funds required to buy
the physical goods, i.e.,
interest.
C. Supply and demand for loanable funds
determine Interest rates.
1. Demand for funds is a function of individual, business, and
government
attitudes toward investment risk.
a. These attitudes determine the required rate of return an
asset must earn to be part of the production process.
b. The more the risk, the higher the required rate of return.
2. Supply of funds is a function of individual, business, and
government saving and Federal Reserve policy.
D. Characteristics of a loanable funds (debt) market
1. Demand comes from the
needs on individuals, business,
and
government to borrow for investments.
2. Supply comes from the
savings of individuals, business,
our
governments, and foreigners who loan us profits from
trading with us.
3. During the 1980's a
dramatic increase in the demand for
loanable funds combined with a decrease in
savings to
yield a dramatic
rise in real interest rates. This increase
caused a decrease in business
capital investment and
slow economic growth.

Enterprise and business profit
A. Economic
profit is revenue minus explicit + implicit costs
B. An amount greater than zero
represents economic rent.
C. Entrepreneurs receive
economic rent for these
activities.
1.
Initiative
2.
Decision making
3.
Innovation
4.
Risk taking
5.
Monopolizing markets
6. Controlling
Government
D. Modern methods of creating rent include
1. domestic
outsourcing
2. inter-firm contracting
3. growing importance of
production networks to
E. Economic profit exists in expanding industries
and
will disappears as a
result of competitive forces
or result in social unrest. See