![]()
Chapter
21 Printable One-Page Review
How Cost of
Production Affects Supply Part 1 See
Part 2
View
Entire Chapter 21
with videos
Defining costs
1. Costs are
the dollars paid for the factors of production.
2. Opportunity
cost is the value of the best alternate use, e.g., the
cost of labor is the value that could have been
received from using capital.
3. Explicit
costs versus implicit costs
a. Explicit
costs require an out-of-pocket expenditure, e.g., wages,
materials, and overhead.
b. Implicit
costs do not require an outlay, e.g., forgone wages for uncompensated efforts
by family members in
a family-operated business, included a normal return
on investment, which is the minimum amount
required
to keep resources employed at their current use.
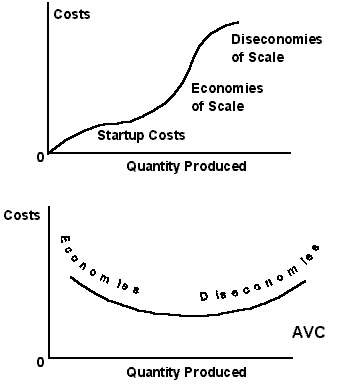
4. Short run costs are both fixed and variable,
in the long run, all costs are variable
a. Fixed
costs do not vary with production, e.g., plant and equipment,
property taxes, most overhead, etc.
b. Variable
costs vary directly with production, e.g., labor and
materials
c.
Marginal
cost is
the change in total costs which resultsfrom
making one more unit.
5. Diminishing
returns:
a. Adding a variable resource (labor) to a fixed resource (capital) will
increase production for a while.
b. At some point the rate of increase declines and eventually becomes
negative.
c. Diminishing returns affect both the production of labor and cost of
production.
d. Example: Using three people to do the dishes didn't make sense because
the third person just got in the way.
Mom did agree so she relaxed.
Accounting profits versus economic profits
1. Accounting profit is
revenue minus explicit costs and economic profit is
revenue minus explicit plus implicit costs.
2 Since implicit cost includes a payment
for the risk factor part of interest and payment for entrepreneurial
skill.
3. This means Normal
Profit is a cost to economists and paid for as an explicit
cost, in the long run competition
causes economic profit to be zero.