IV.
Monopolistic Competition
View Entire Chapter 25
A. A monopolistically competitive market
exists when a substantially large
number of firms serve a market with relatively differentiated products.
B. Examples are merchandising selling shoes, shirts,
TV's, groceries,
etc.
C. Product differentiation
1.For some
it is real, important, for others it's artificial,
unimportant.
a.
Non-price competition differentiators
1.
Product quality
2.
Product image (Branding)
3.
Customer service
4.
Store environment and image
b.
Condition for sale (location)
1.
Mail order
2.
Home delivery using the internet
3. Bidding on the internet
C. Some control over price exists and demand tends
to be more elastic
than with monopoly or oligopoly markets.
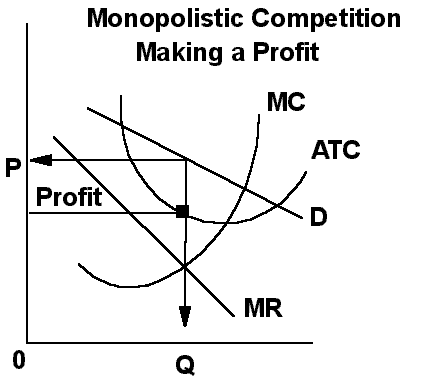
D. Economic analysis of monopolistic competition
1. P is high compared to pure
competition (P> MR = MC)
2. Quantity will be restricted
causing ATC to be higher than that
indicated by the curve's lowest point.
3. Tends to be more competitive
than monopoly and oligopoly.
4. Some believe economic profit
tends toward zero as the number
of firms adjust to varying
profit levels.
VI. An oligopoly market exists
when barriers to entry result in a
few mutually dependent
companies controlling
a substantial portion of a market.
A. Products may be
homogeneous or differentiated.
B. Examples include many
industrial products such as steel
and large consumer
durables such as appliances.
C. Automobile, steel, game
consoles and
other oligopolistic
industries lost
monopoly power because of the foreign invasion of the 1970's.
D.
Economic analysis of oligopoly
1. Restrictive
oligopolies tend to be very monopolistic in nature with
a.
P > MR = MC
b.
Production is not at the lowest point indicated by the ATC curve.
c.
Economic profits exist and quantity is restricted.
2. Progressive oligopolies
have high economic profits in spite
of price decreases
brought on by high-tech efficiencies.
|
V. Oligopoly
View
Entire Chapter 26
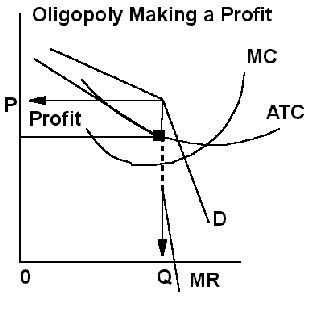
A. An oligopoly market exists
when barriers to entry result in a few producers.
1. Products may be
homogeneous or
differentiated.
2. Examples include many industrial products such as steel and consumer
goods like soda.
3. Automobile, steel,
game
consoles and
other oligopolistic industries lost monopoly power
because of the foreign
invasion beginning in the 1970's.
a. Eventually American companies became more competitive.
b. The price was lower real wages for manufacturing workers.
c.
The
oligopolistic nature of the video game consol market
4.
Concentration ratios
measure the amount of total output controlled by a few firms.
a.
eight-firm concentration ratio - Amosweb is Economics ..
b.
four-firm concentration ratio -Amosweb
5. Readings
a. Six
movie studios movie studios receive
90% of American film revenues.
b. The television industry is mostly an oligopoly of five companies:
Disney/ABC
,
CBS
c.
NBC
Universal
Time
Warner and
News Corporation See
Concentration of media ownership
.
d. Four major
music companies receive 80% of recording
revenues.
e. Four wireless providers control 89% of the cellular telephone market.
f. There are just six major book publishers.
g. Healthcare insurance in the United States consists of very few insurance
companies controlling
major market share in most states. For example, California's insured population of 20 million is
the most
competitive in the nation and 44% of that market is dominated by two insurance
companies, Anthem and
Kaiser Permanente.
h.
Anheuser-Busch and
Miller Coors control about 80% of the
beer industry.
B.
Three well-defined pricing models exist
1. Kinked
demand
2. Collusive pricing
3. Price
leadership
Please |