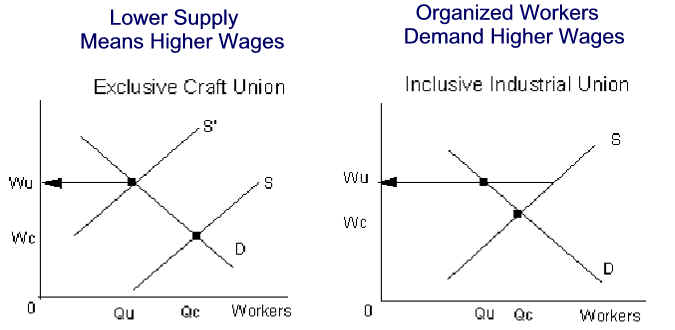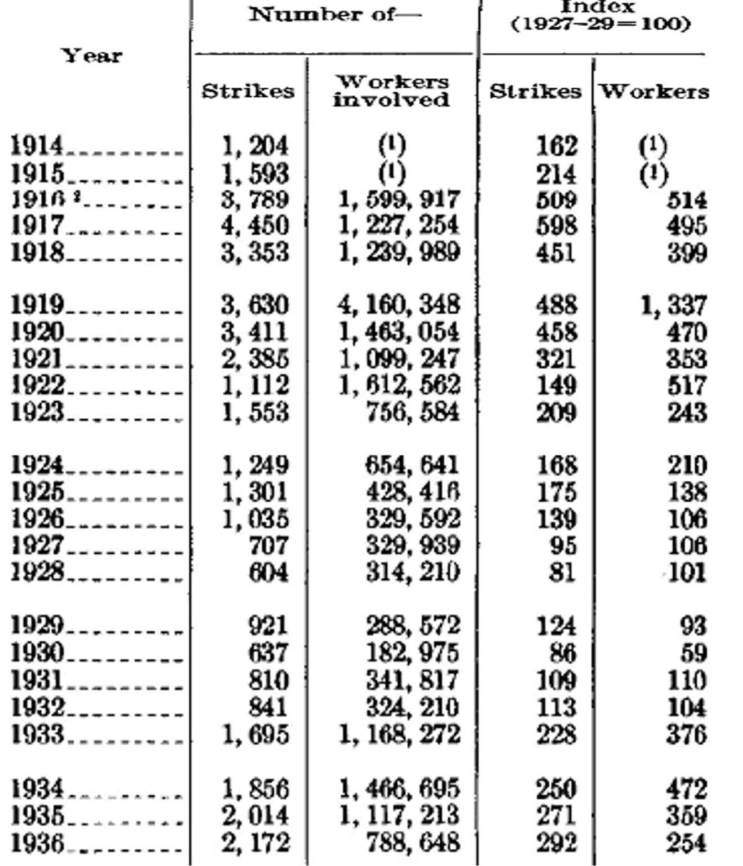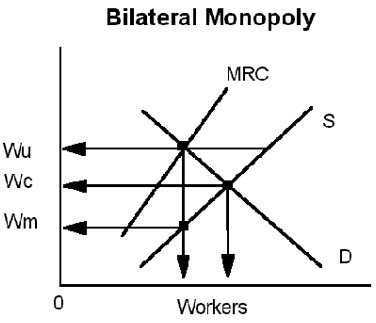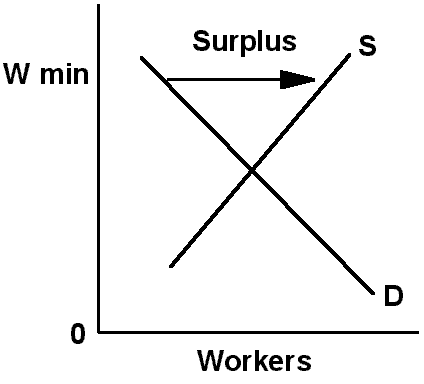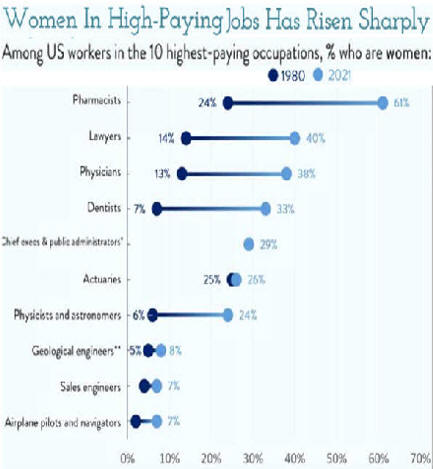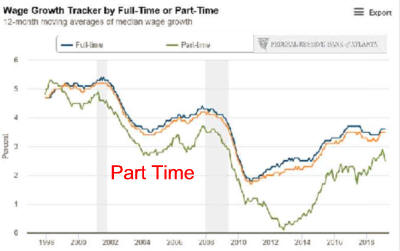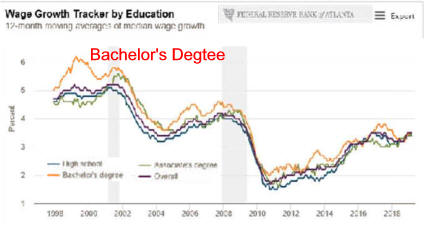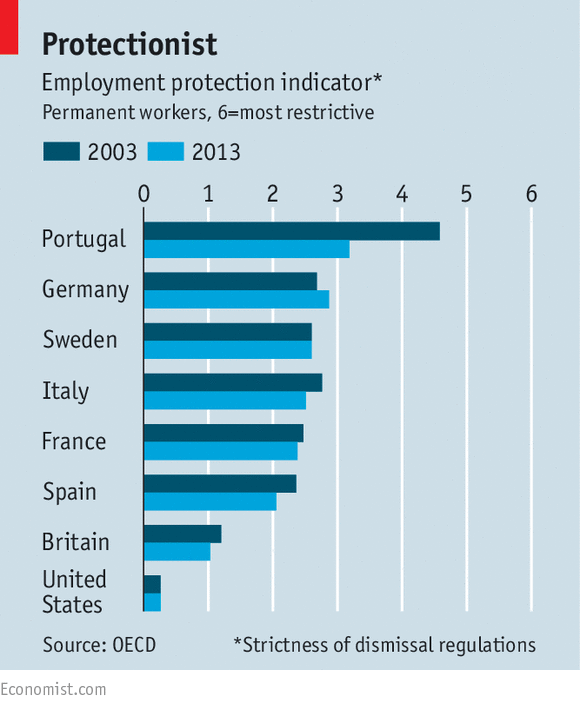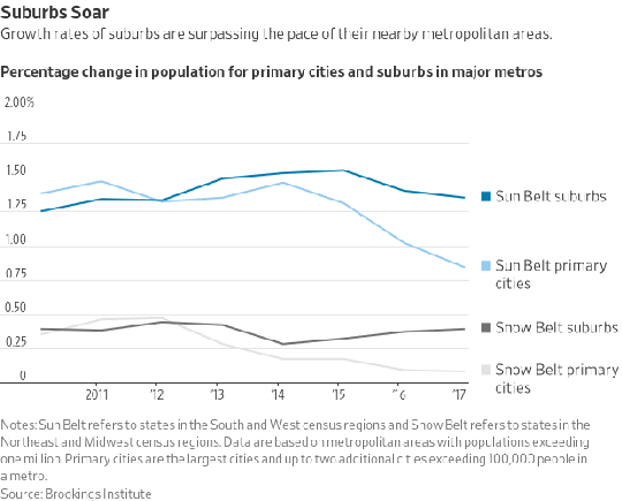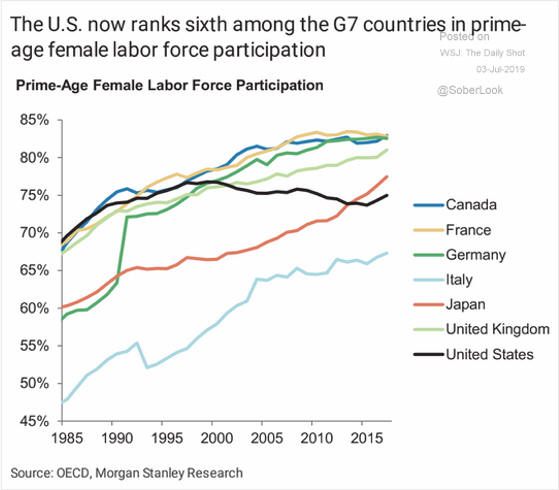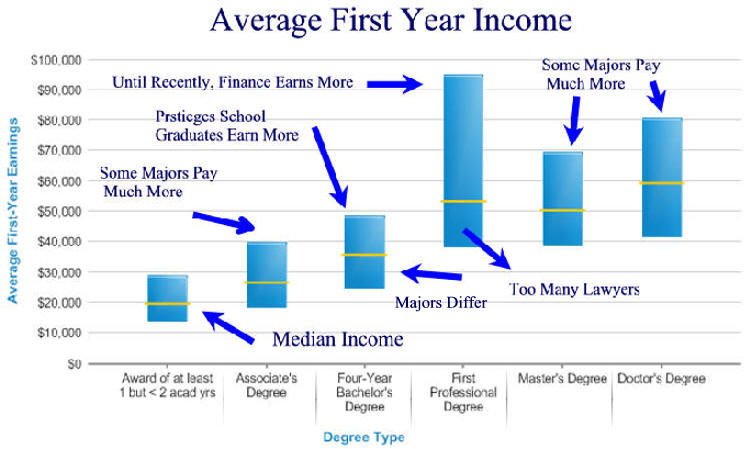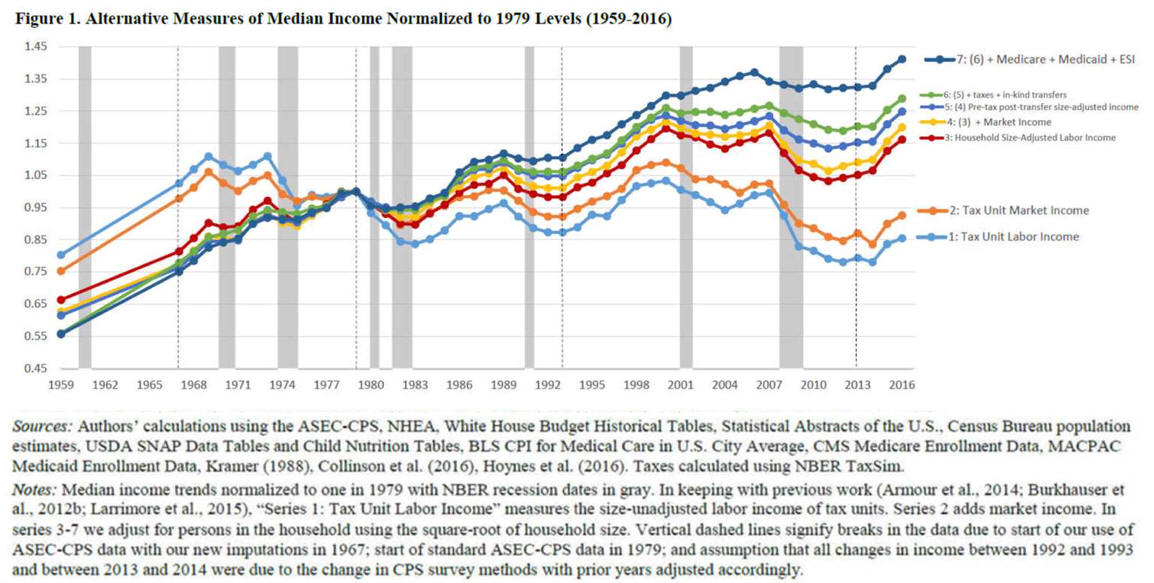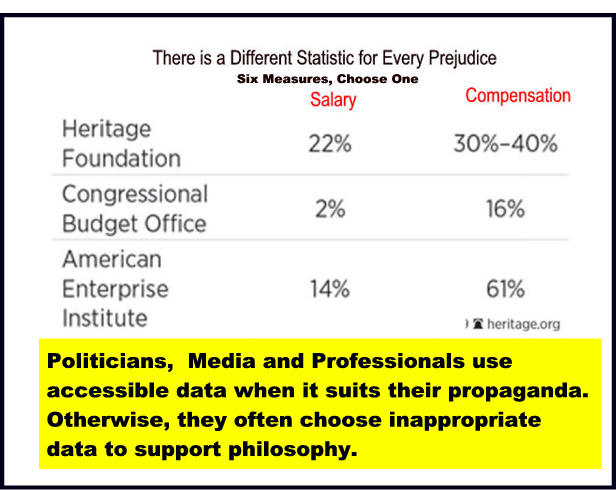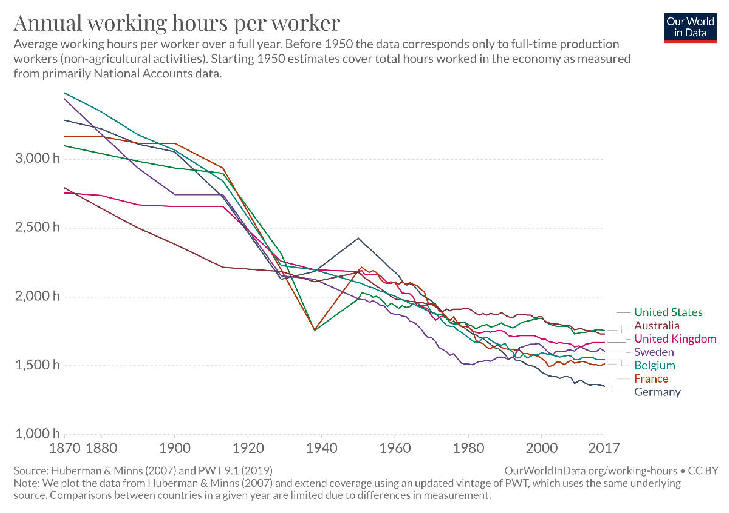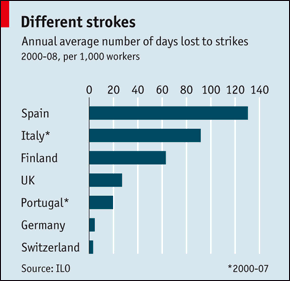


|
|
|
|
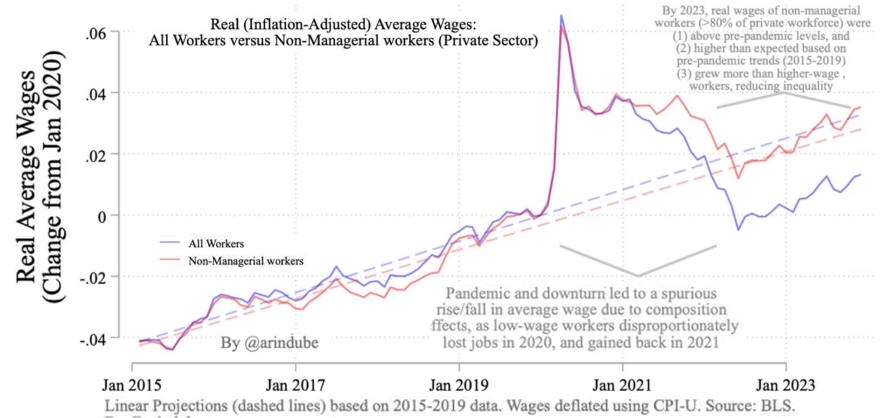
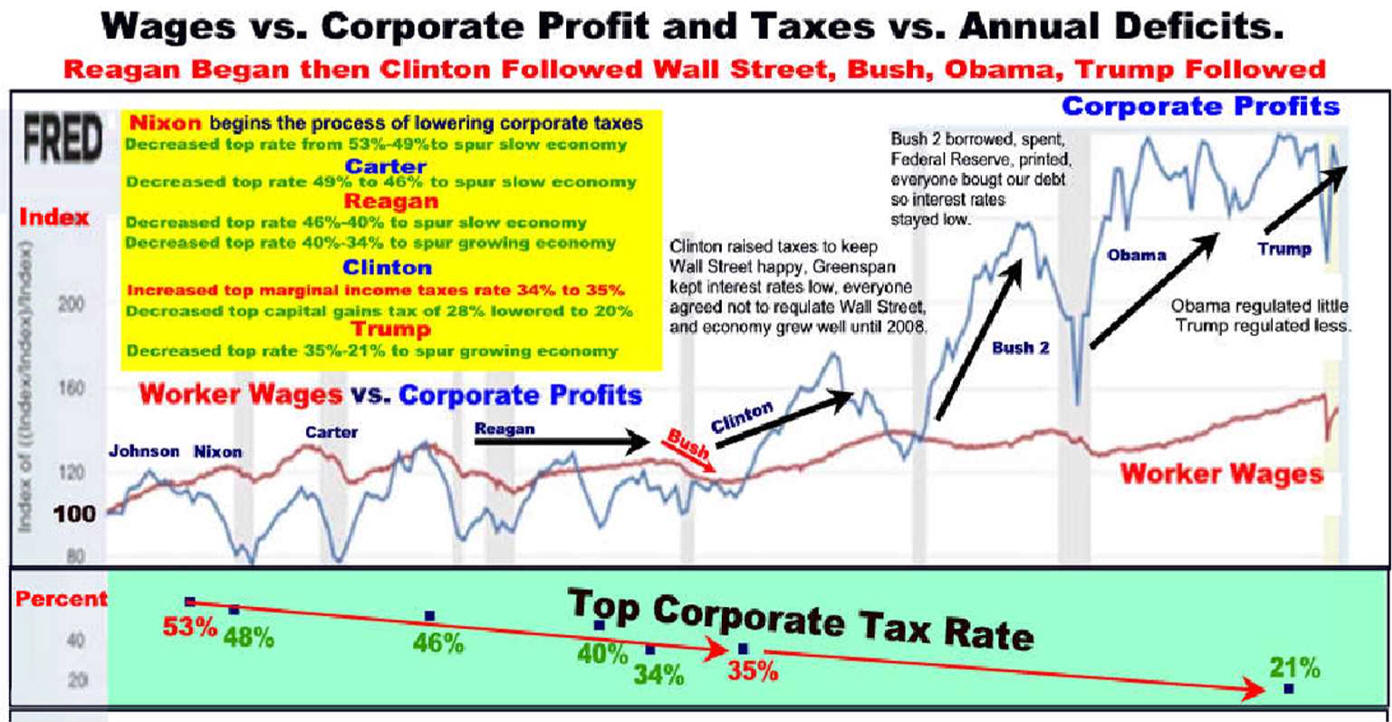
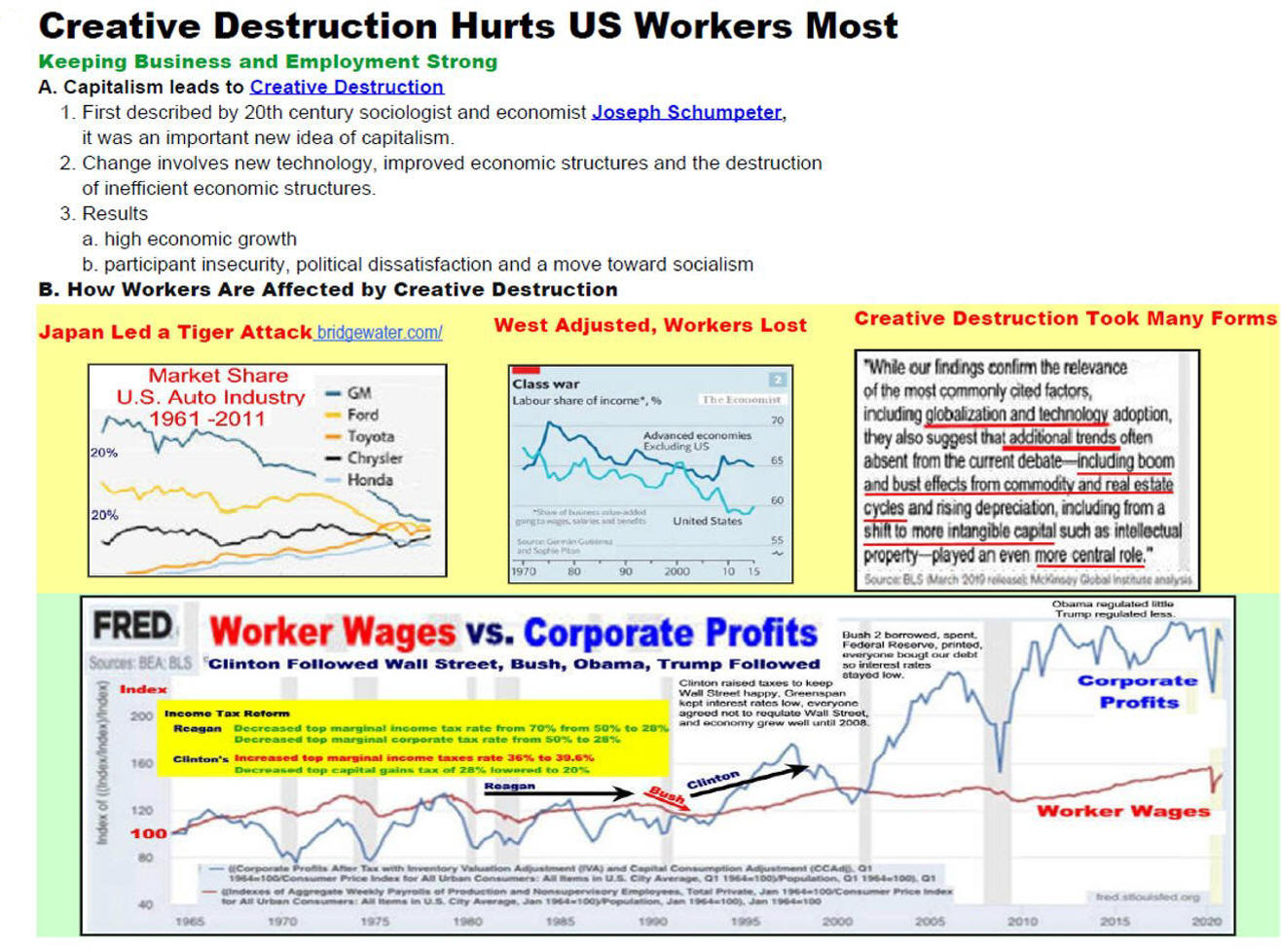
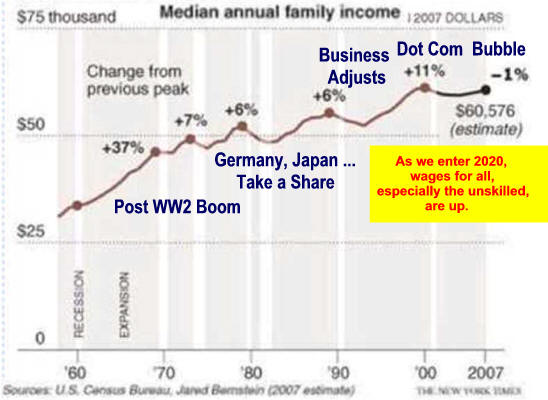
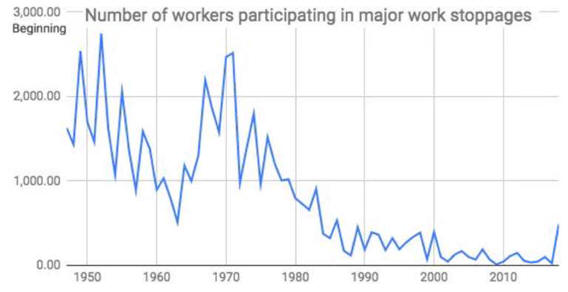
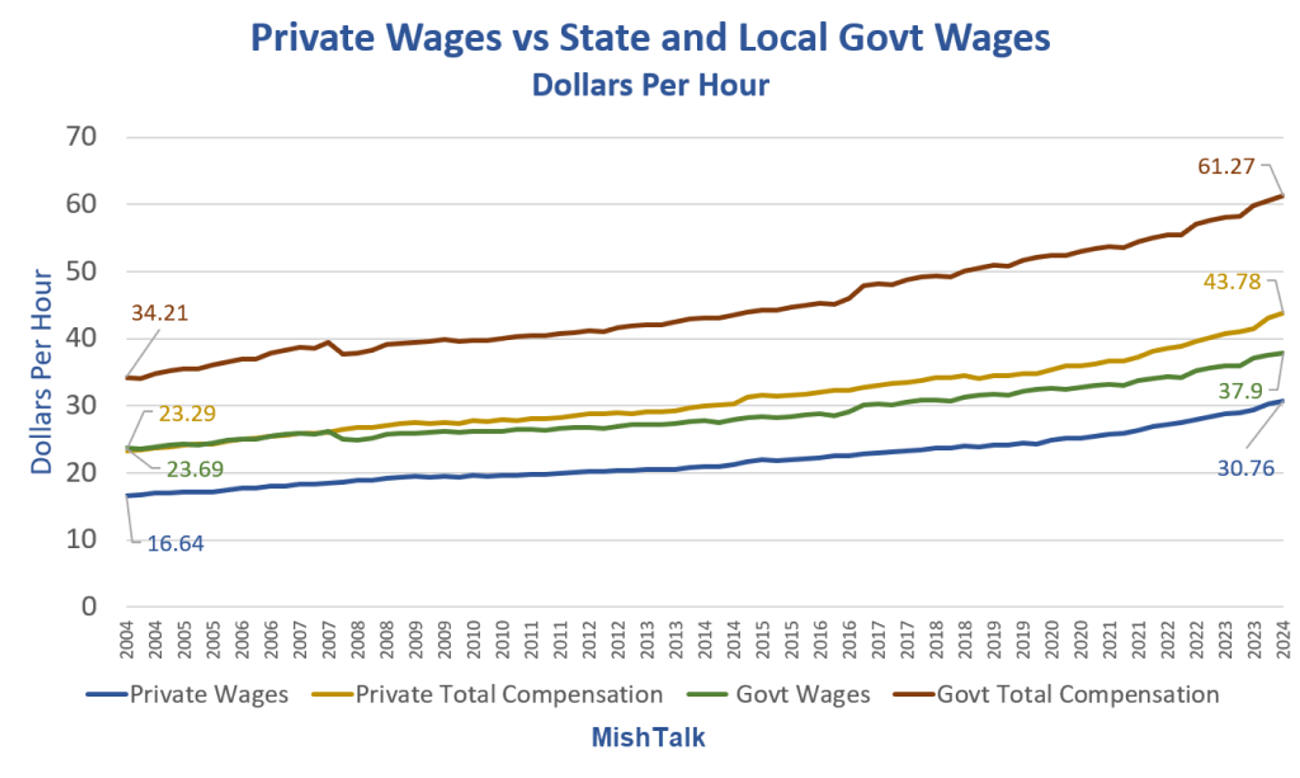
Wage Growth Has Been Steady
|
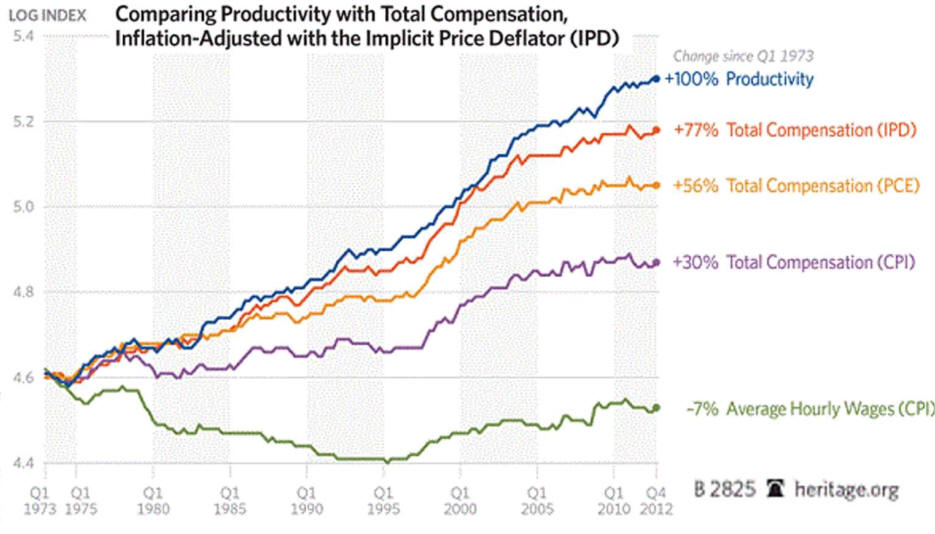
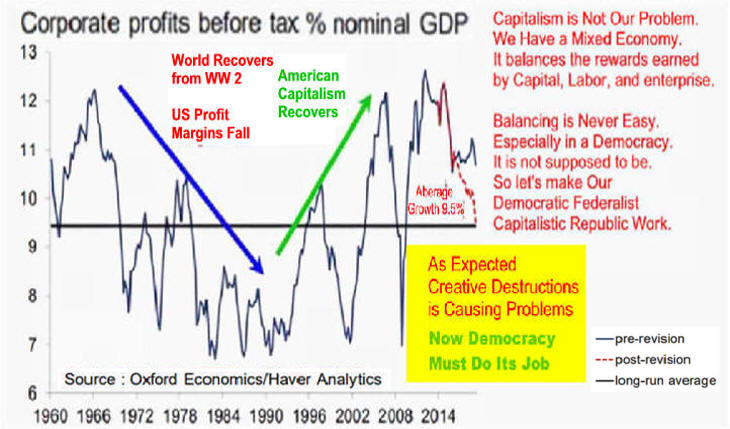
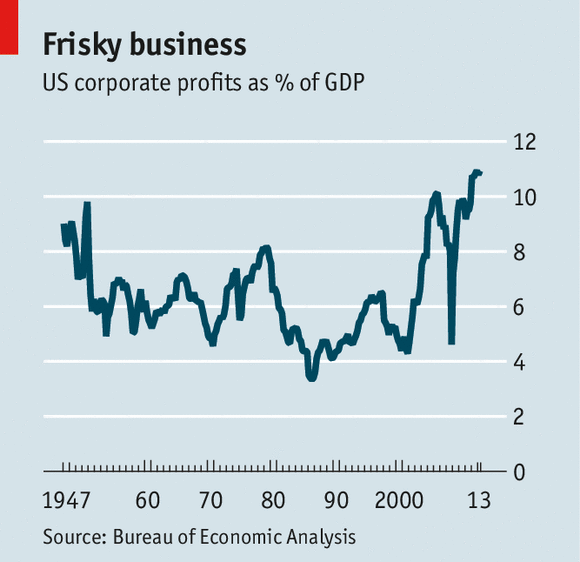
Corporate Profits are
Volatile
|
|
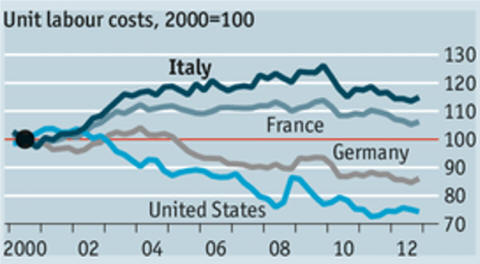
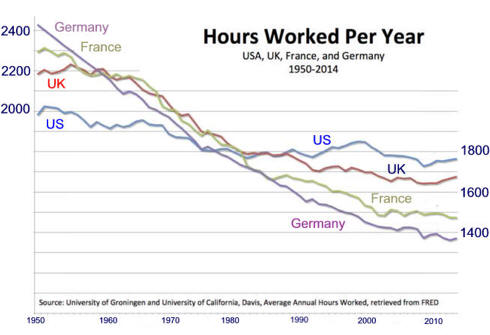
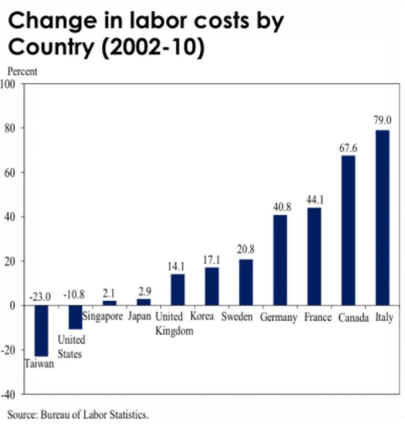
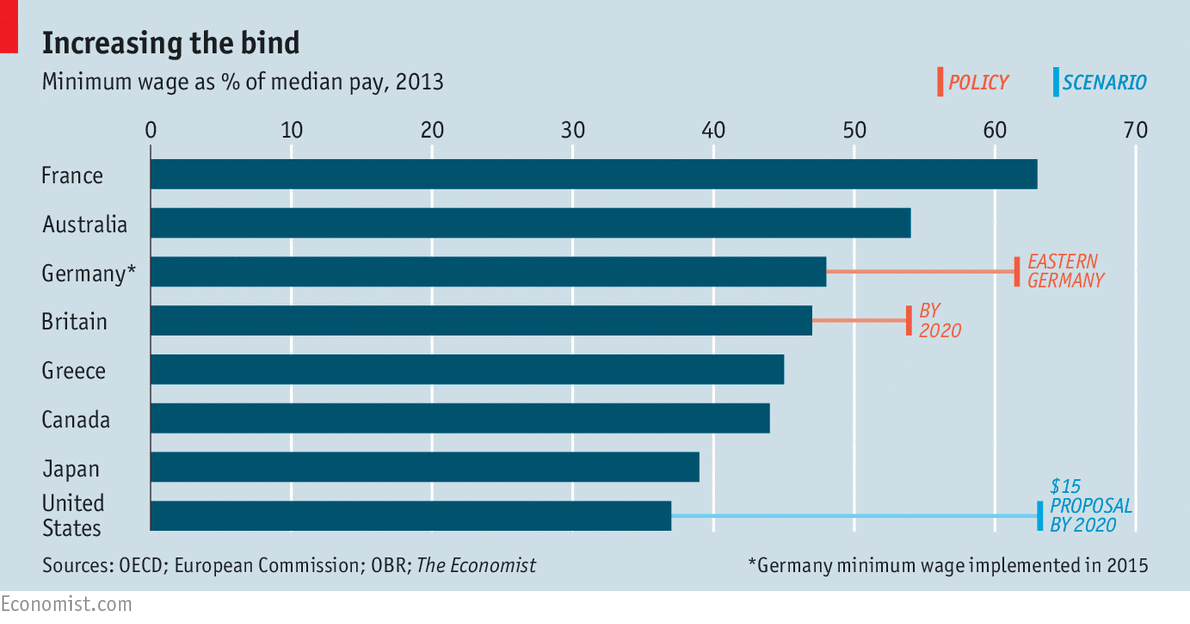
E. Competitive countries, to
keep market share
Germany has a wage share
system.
The
Economist Magazine
5/4/13
Please
Share! |
|
|
|
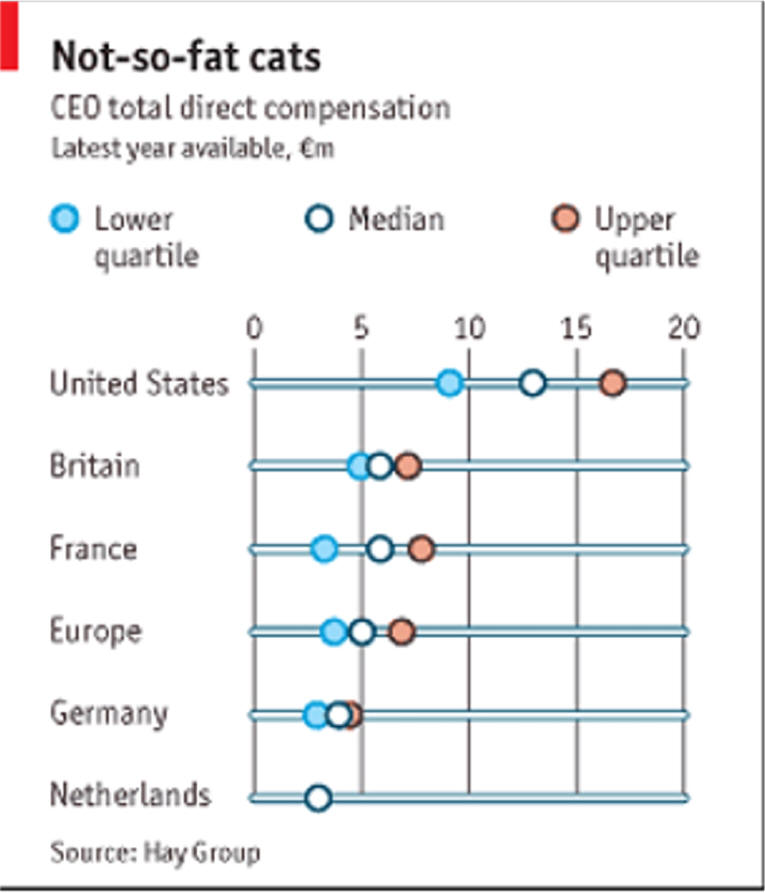
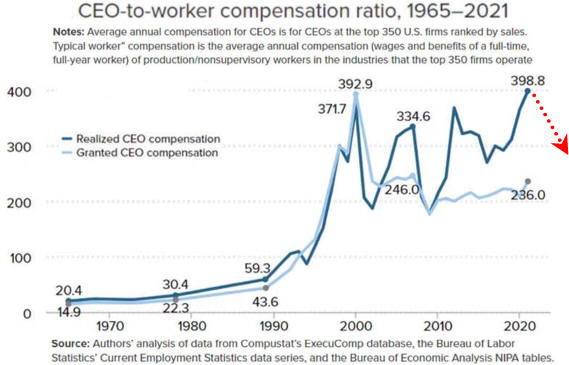
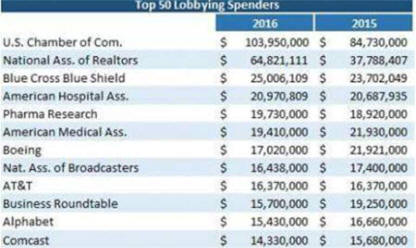
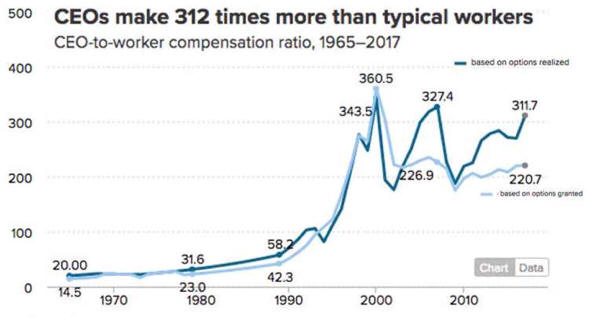
CEO's Got Lots
|
|
|
|
|
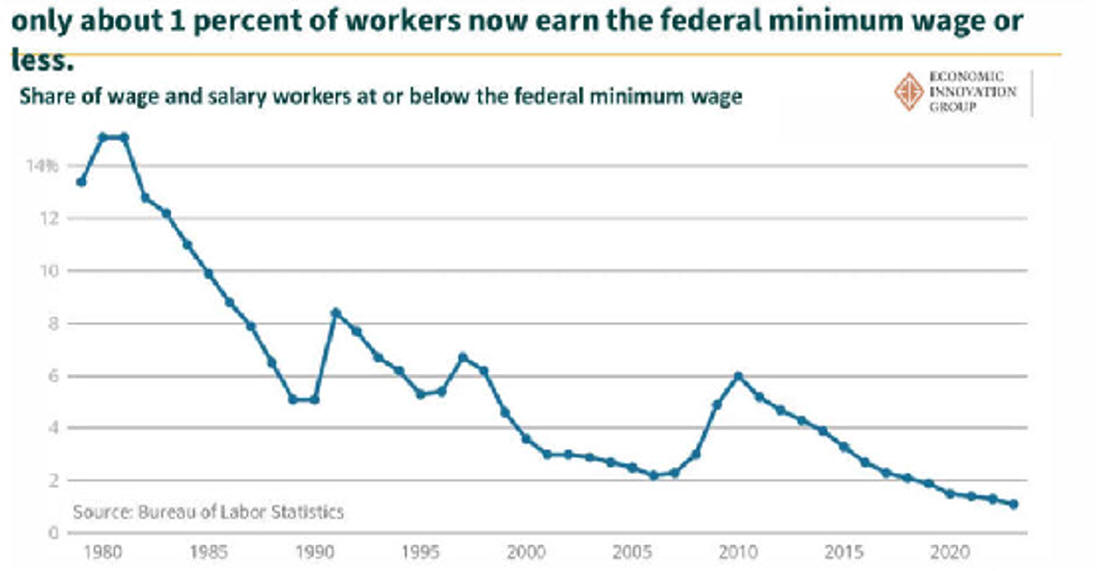
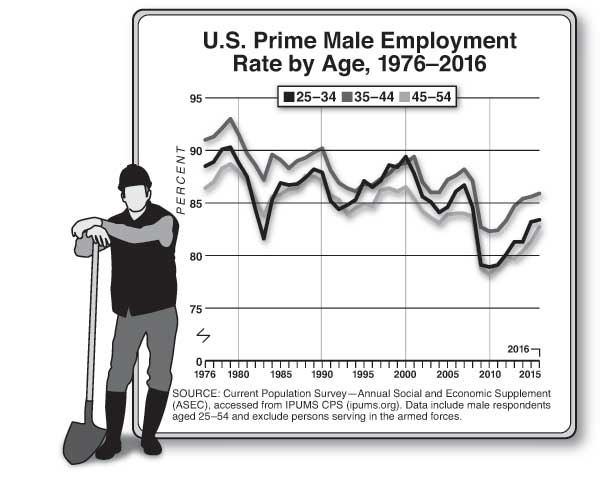
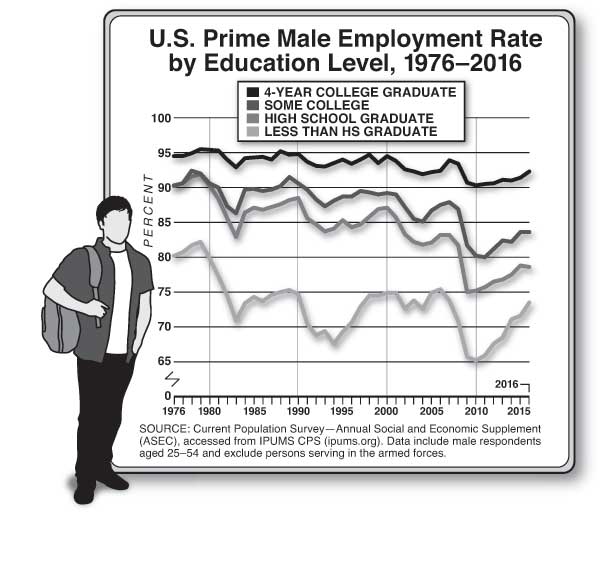
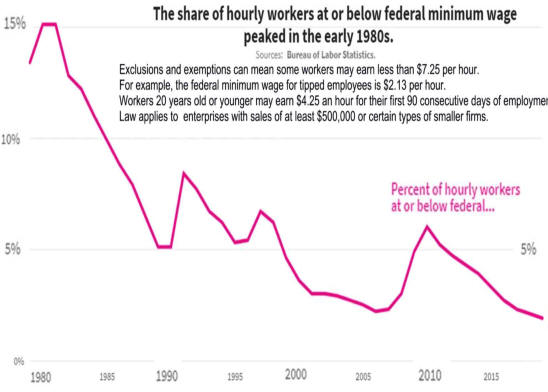
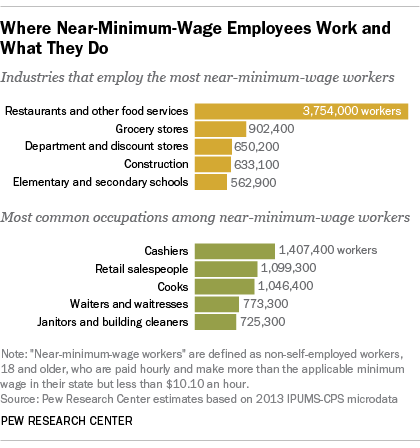
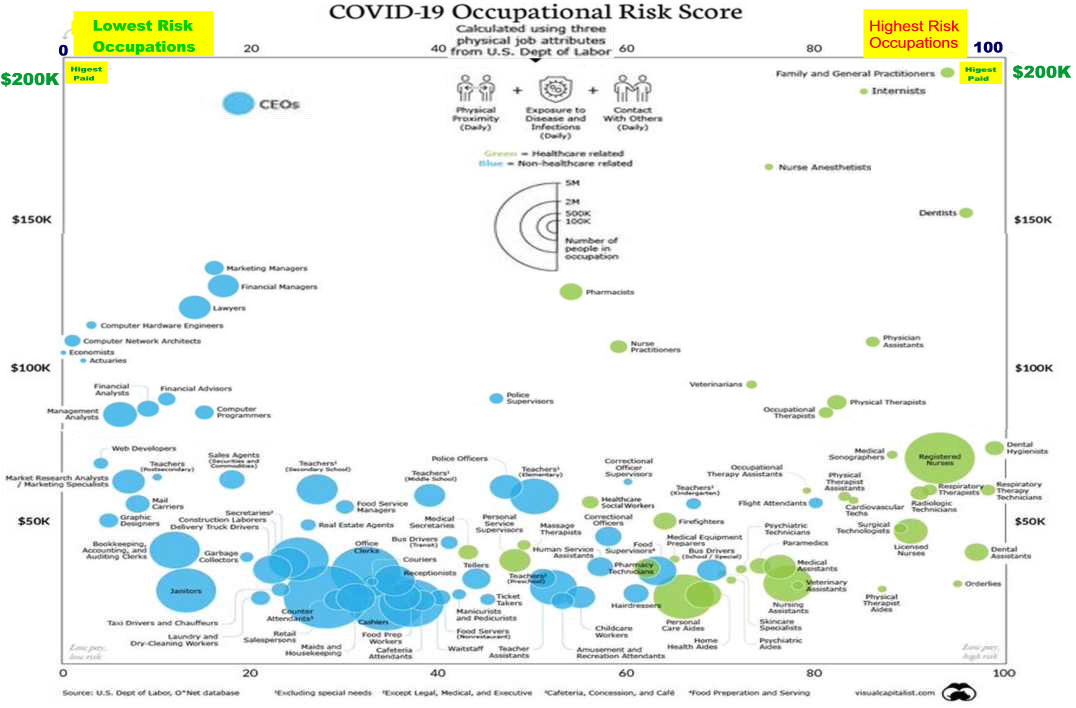
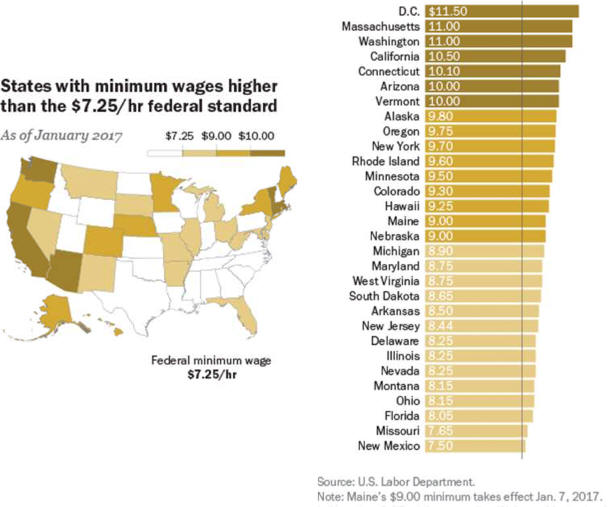
The War on Work—and How to End It Unfortunately, policymakers seem intent on making the joblessness crisis worse. The past decade or so has seen a resurgent progressive focus on inequality—and little concern among progressives about the downsides of discouraging work. Advocates of a $15 minimum hourly wage, for example, don’t seem to mind, or believe, that such policies deter firms from hiring less skilled workers. The University of California–San Diego’s Jeffrey Clemens examined states where higher federal minimum wages raised the effective state-level minimum wage during the last decade. He found that the higher minimum “reduced employment among individuals ages 16 to 30 with less than a high school education by 5.6 percentage points,” which accounted for “43 percent of the sustained, 13 percentage point decline in this skill group’s employment rate.” The decision to prioritize equality over employment is particularly puzzling, given that social scientists have repeatedly found that unemployment is the greater evil. Economists Andrew Clark and Andrew Oswald have documented the huge drop in happiness associated with unemployment—about ten times larger than that associated with a reduction in earnings from the $50,000–$75,000 range to the $35,000–$50,000 bracket. One recent study estimated that unemployment leads to 45,000 suicides worldwide annually. Jobless husbands have a 50 percent higher divorce rate than employed husbands. The impact of lower income on suicide and divorce is much smaller. The negative effects of unemployment are magnified because it so often becomes a semi permanent state. Time-use studies help us understand why the unemployed are so miserable. Jobless men don’t do a lot more socializing; they don’t spend much more time with their kids. They do spend an extra 100 minutes daily watching television, and they sleep more. The jobless also are more likely to use illegal drugs. While fewer than 10 percent of full-time workers have used an illegal substance in any given week, 18 percent of the unemployed have done drugs in the last seven days, according to a 2013 study by Alejandro Badel and Brian Greaney. Joblessness and disability are also particularly associated with America’s deadly Opioid epidemic. David Cutler and I examined the rise in Opioid deaths between 1992 and 2012. The strongest correlate of those deaths is the share of the population on disability. That connection suggests a combination of the direct influence of being disabled, which generates a demand for painkillers; the availability of the drugs through the health-care system; and the psychological misery of having no economic future. Increasing the benefits received by nonemployed persons may make their lives easier in a material sense but won’t help reattach them to the labor force. It won’t give them the sense of pride that comes from economic independence. It won’t give them the reassuring social interactions that come from workplace relationships. When societies sacrifice employment for a notion of income equality, they make the wrong choice. Politicians, when they do focus on long-term unemployment, too often advance poorly targeted solutions, such as faster growth, more infrastructure investment, and less trade. More robust GDP growth is always a worthy aim, but it seems unlikely to get the chronically jobless back to work. The booms of the 1990s and early 2000s never came close to restoring the high employment rates last seen in the 1970s. Between 1976 and 2015, Nevada’s GDP grew the most and Michigan’s GDP grew the least among American states. Yet the two states had almost identical rises in the share of jobless prime-age men. Infrastructure spending similarly seems poorly targeted to ease the problem. Contemporary infrastructure projects rely on skilled workers, typically with wages exceeding $25 per hour; most of today’s jobless lack such skills. Further, the current employment in highway, street, and bridge construction in the U.S. is only 316,000. Even if this number rose by 50 percent, it would still mean only a small reduction in the millions of jobless Americans. And the nation needs infrastructure most in areas with the highest population density; joblessness is most common outside metropolitan America. (See “If You Build It . . .,” Summer 2016.) Finally, while it’s possible that the rise of American joblessness would have been slower if the U.S. had weaker trade ties to lower-wage countries like Mexico and China, American manufacturers have already adapted to a globalized world by mechanizing and outsourcing. We have little reason to be confident that restrictions on trade would bring the old jobs back. Trade wars would have an economic price, too. American exporters would cut back hiring. The cost of imported manufactured goods would rise, and U.S. consumers would pay more, in exchange for—at best—uncertain employment gains. The techno-futurist narrative holds that machines will displace most workers, eventually. Social peace will be maintained only if the armies of the jobless are kept quiet with generous universal-income payments. This vision recalls John Maynard Keynes’s 1930 essay “Economic Possibilities for Our Grandchildren,” which predicts a future world of leisure, in which his grandchildren would be able to satisfy their basic needs with a few hours of labor and then spend the rest of their waking hours edifying themselves with culture and fun. But for many of us, technological progress has led to longer work hours, not playtime. Entrepreneurs conjured more products that generated more earnings. Almost no Americans today would be happy with the lifestyle of their ancestors in 1930. For many, work also became not only more remunerative but more interesting. No Pennsylvania miner was likely to show up for extra hours (without extra pay) voluntarily. Google employees do it all the time.
|
Joblessness is not foreordained, because entrepreneurs can always dream up new ways of making labor productive. Ten years ago, millions of Americans wanted inexpensive car service. Uber showed how underemployed workers could earn something providing that service. Prosperous, time-short Americans are desperate for a host of other services—they want not only drivers but also cooks for their dinners and nurses for their elderly parents and much more. There is no shortage of demand for the right kinds of labor, and entrepreneurial insight could multiply the number of new tasks that could be performed by the currently out-of-work. Yet over the last 30 years, entrepreneurial talent has focused far more on delivering new tools for the skilled than on employment for the unlucky. Whereas Henry Ford employed hundreds of thousands of Americans without college degrees, Mark Zuckerberg primarily hires highly educated programmers. Unfortunately, policymakers seem intent on making the joblessness crisis worse. Little concern among progressives about the downsides of discouraging work. Jeffrey Clemens increase state-level minimum wage during the last
decade.
"huge drop in happiness associated with unemployment—about ten times larger than that associated with a reduction in earnings from the $50,000–$75,000 range to the $35,000–$50,000 bracket. One recent study estimated that unemployment leads to 45,000 suicides worldwide annually. Jobless husbands have a 50 percent higher divorce rate than employed husbands. The impact of lower income on suicide and divorce is much smaller. The negative effects of unemployment are magnified because it so often becomes a semi permanent state." Increasing the benefits received by nonemployed persons may make their lives easier in a material sense but won’t help reattach them to the labor force Joblessness and disability are also particularly associated with America’s deadly Opioid epidemic.
|
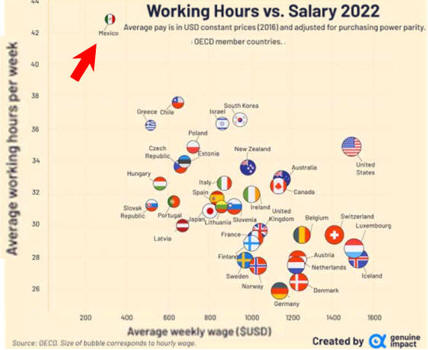
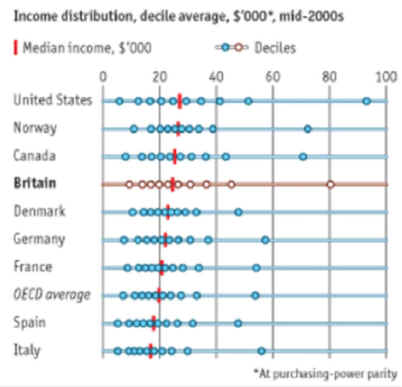
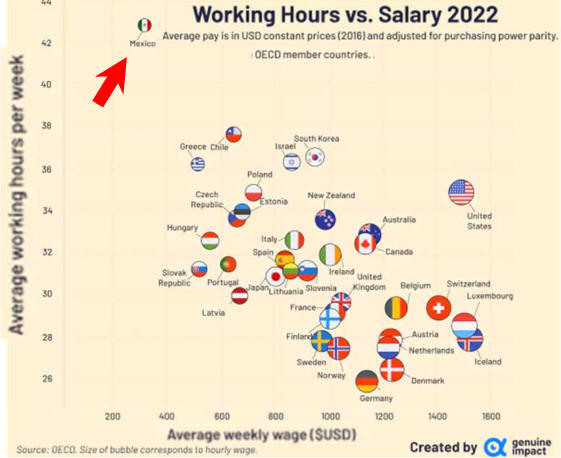
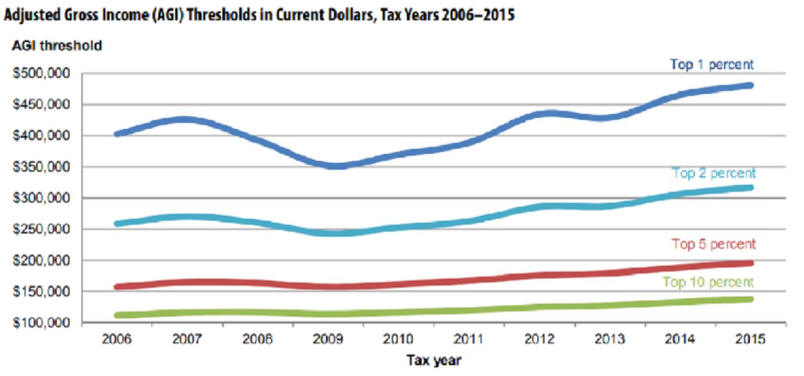
Data are in
United States dollars at current prices
and current
purchasing power parity for the reference year.
|
From
The Story of the American Recovery in 15 charts |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||