|
Lecture Notes
1-page
printable lecture notes
I. Basic Terms
A. Economy is the social science
concerned with the use of
resources like land
and labor to fulfill human needs.
B.
Resources are the inputs, want satisfaction is the output
C. Key Concepts for understanding and analysis
1. Scarcity of resources
results in the need for choices by participants.
2. Purposeful behavior by
participants
(buyers
and sellers) is exhibited
to enhance their own rational
self interest.
See
Economics in the dock 6 min video
3. Marginal
analysis where the change in benefit received is balanced
with the change in cost is a
common purposeful behavior.
See
Margins
and Thinking at the Margin
4. Fallacy
of composition: applying to the whole that which is true for
a part without adequate proof. 1 and
3 are odd numbers, so four is
odd number.
This fallacy is the basis of police profiling.
See
Why Do People Continue to Believe Stupid Economic Ideas
-
Mark Blyth
5 min
video
5.
Fallacy of
division:
This is the assumption that if something is
true
for the whole then it must be true
for its parts.
The absolutely worst
abuse here involves inferring from an
average that all elements are
average.
6. Post
hoc fallacy: Assumption
that correlation proves causation.
This is related to the concept in law
of circumstantial evidence.
7. Cum
Hoc Fallacy :simultaneous correlations while post hoc refers
to sequential
correlations.
8.
Logical fallacies
is
a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw
in its
logical structure
that can neatly be expressed in a standard
logic system
D. Economic methodology
1. Positive
economics
a.
What something is
b.
Objective, can be measured
c.
Example: measuring disposable personal income which is an
individual's salary after taxes
d. A
Theorem on the Methodology of Positive Economics
e.
Inflation Binary
2. Normative
economics
a.
What something ought to be
b.
Subjective, difficult to measure
c.
Requires value judgments by citizens, Political Action Committees
(PAC's),
politicians, economists, etc.
d. Examples: should the minimum wage be increased,
should
defense spending
increase and social spending be lowered
3.
Descriptive economics
a.
Looking at the real-world to develop Economic Theory
b. Economic
Theory
1. Generalizations concerning economic behavior based upon
real
-world
observations, empirical by nature
2. Economic theories are objective "positive economics"
3. Assumes behavior is rational and economic (self-serving)
4. Example: as the price of a product increases, consumers tend
to buy less
c. Economic Policy
1. Application of economic theory to solve economic problems
2. Economic policies are subjective, "normative economics".
3. How society makes economic choices such as in the 1980's
when spending
for the elderly (Social Security) increased
and spending for children
(Head Start) decreased 1234
4. Using Statistics
1. Why Do Economists Use Statistics?
2. Common Errors
interpreting Statistics
3.
Beginning with video 3 the series, statistics
are used in a questionable manner to analyze
to current economic issues of concern to Libertarians.
II.
Economic
Models
A.
Definition
1. Simplified
generalizations to represent of real-world economic activity
2. Requires Ceteris Paribus: Latin for holding other
economic variables constant
See
Ceteris Paribus
Trap
B.
Designing Models
1. Models may be quantities or qualitative
2. Economic
Models 3 minute video
3. Three Pitfalls
to model analysis
a. Restrictive, unrealistic assumptions
b. Omitted details
c. Are economic models falsifiable?
4. Model representations are not
always correct
a.
Are economic models falsifiable?
b.
Pfleiderer on The Misuse of Economic Models 1 hour podcast
c. Models such as the Production Possibility Curve
chapter 2 and supply
and demand, chapter 3, explained in the next chapter
provide a simplified
description of how some aspect of an economy works.
d.
Beware of economic textbooks
11/30/14
e.
Why Do People Continue To Believe Stupid Economic Ideas? 4/17 Mark Blyth
g.
Economics Rules: the rights and wrongs of the dismal science
h.
Economists And Statistical Tests Are Bias
4/3/18
III. United States Economic Goals
A.
Employment
Act of 1946 set goals in response to a
Soviet 5-year
economic plans.
B.
Humphrey
Hawkins Act of 1978 added goals.
1. Economic growth
2. Full employment of all
economic resources
3. Price stability (low
inflation)
4. Positive balance of payments
(international flow of dollars)
5. Economic freedom
6. Equitable distribution of
income
7. Economic security (if you have A
through F, you have G)
C.
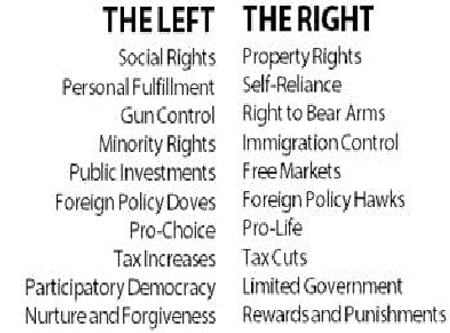
Political Goals Differ
D. Economic Report of the President
|
Political Economy
Stuff

 |
|
Conservatism
from
Conservative Sensibility
by
George Will
Based on US Declaration of Independence
"We hold these truths to be self-evident,
that all
men are created equal,
that they are endowed by their Creator with certain
unalienable
Rights,
that among these are
Life, Liberty and the
pursuit of Happiness. —
That to secure these rights,
Governments are instituted among Men,
deriving their just powers
from the consent
of the governed..."
|
|
Progressivism
Inspired by
American Nations by
Golin Woodard
Based on US Constitution
"We the
People of the United States,
in Order to form a more perfect Union,
establish justice, insure domestic
Tranquility,
provide for the common defense,
promote the general Welfare,
and secure the Blessings of Liberty
to ourselves and our Posterity,
do ordain and establish this Constitution
for the United States of America." |
|
 |

See
US Constitutional History
from
Magna Carte to Trump's SC Battle
US History: A Constitutional; Approach
Jamestown
to Selma, Alabama
7/14/23
|
