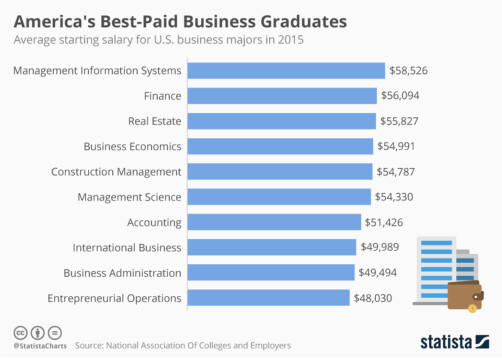
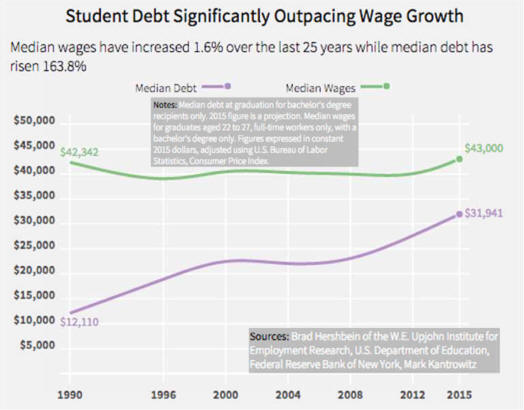
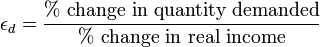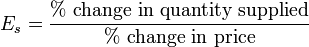| F. Tax
Incidence Effects
PEDs, in combination with
price
elasticity of supply (PES), can be used to assess where the
incidence (or "burden") of a per-unit tax is falling or to
predict where it will fall if the tax is imposed. For example, when
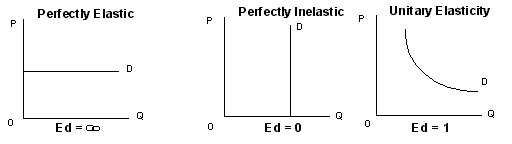
demand is perfectly inelastic, by definition consumers have no
alternative to purchasing the good or service if the price increases, so
the quantity demanded would remain constant. Hence, suppliers can
increase the price by the full amount of the tax, and the consumer would
end up paying the entirety. In the opposite case, when demand is perfectly
elastic, by definition consumers have an infinite ability to switch
to alternatives if the price increases, so they would stop buying the
good or service in question completely—quantity demanded would fall to
zero. As a result, firms cannot pass on any part of the tax by raising
prices, so they would be forced to pay all of it themselves.[38]
More generally, then, the higher
the elasticity of demand compared to PES, the heavier the burden on
producers; conversely, the more inelastic the demand compared to
PES, the heavier the burden on consumers. The general principle is that
the party (i.e., consumers or producers) that has fewer
opportunities to avoid the tax.
In practice, demand is likely to be only relatively elastic or
relatively inelastic, that is, somewhere between the extreme cases of
perfect elasticity or inelasticity. ACDC Videos Tax Incidence Taxes on Producers Excise Tax
Practice
|
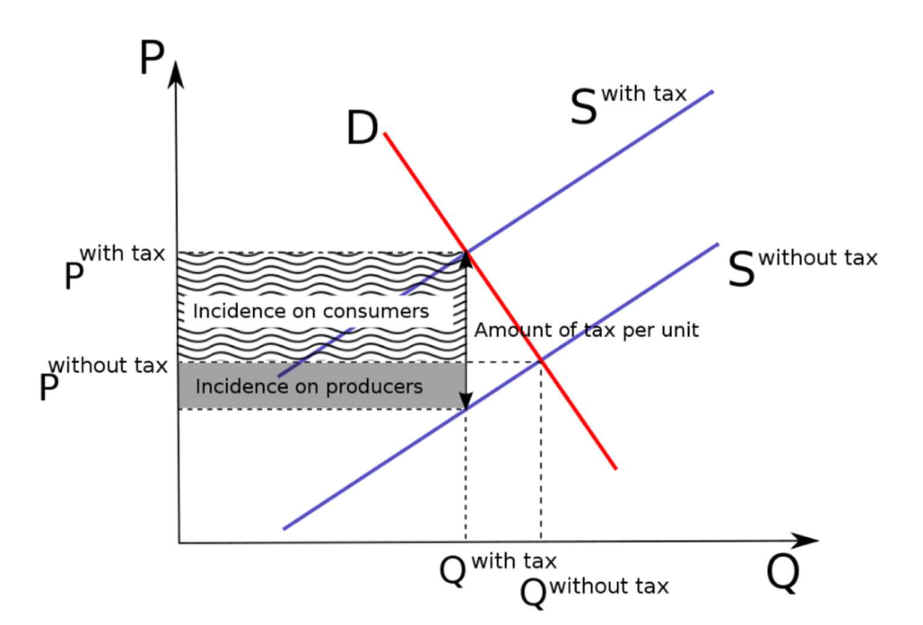
|